Heterodimerization within the TREK channel subfamily produces a diverse family of highly regulated potassium channels
- PMID: 27035963
- PMCID: PMC4839437
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1522459113
Heterodimerization within the TREK channel subfamily produces a diverse family of highly regulated potassium channels
Abstract
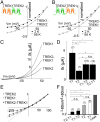
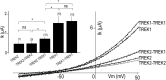
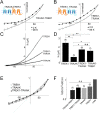
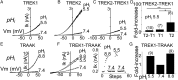
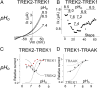
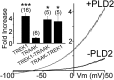
Twik-related K(+) channel 1 (TREK1), TREK2, and Twik-related arachidonic-acid stimulated K(+) channel (TRAAK) form the TREK subfamily of two-pore-domain K(+) (K2P) channels. Despite sharing up to 78% sequence homology and overlapping expression profiles in the nervous system, these channels show major differences in their regulation by physiological stimuli. For instance, TREK1 is inhibited by external acidification, whereas TREK2 is activated. Here, we investigated the ability of the members of the TREK subfamily to assemble to form functional heteromeric channels with novel properties. Using single-molecule pull-down (SiMPull) from HEK cell lysate and subunit counting in the plasma membrane of living cells, we show that TREK1, TREK2, and TRAAK readily coassemble. TREK1 and TREK2 can each heterodimerize with TRAAK, but do so less efficiently than with each other. We functionally characterized the heterodimers and found that all combinations form outwardly rectifying potassium-selective channels but with variable voltage sensitivity and pH regulation. TREK1-TREK2 heterodimers show low levels of activity at physiological external pH but, unlike their corresponding homodimers, are activated by both acidic and alkaline conditions. Modeling based on recent crystal structures, along with mutational analysis, suggests that each subunit within a TREK1-TREK2 channel is regulated independently via titratable His. Finally, TREK1/TRAAK heterodimers differ in function from TRAAK homodimers in two critical ways: they are activated by both intracellular acidification and alkalinization and are regulated by the enzyme phospholipase D2. Thus, heterodimerization provides a means for diversifying functionality through an expansion of the channel types within the K2P channels.
Keywords: combinatorial diversity; heteromerization; leak current; potassium channels; single-molecule fluorescence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
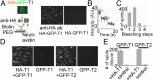
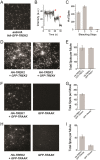
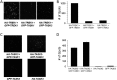
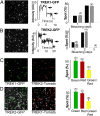

Similar articles
-
Neuronal microRNAs modulate TREK two-pore domain K+ channel expression and current density.RNA Biol. 2020 May;17(5):651-662. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2020.1722450. Epub 2020 Feb 10. RNA Biol. 2020. PMID: 31994436 Free PMC article.
-
β-COP Suppresses the Surface Expression of the TREK2.Cells. 2023 May 29;12(11):1500. doi: 10.3390/cells12111500. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37296621 Free PMC article.
-
Mixing and matching TREK/TRAAK subunits generate heterodimeric K2P channels with unique properties.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Apr 12;113(15):4200-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1522748113. Epub 2016 Mar 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27035965 Free PMC article.
-
How ion channels sense mechanical force: insights from mechanosensitive K2P channels TRAAK, TREK1, and TREK2.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2015 Sep;1352:20-32. doi: 10.1111/nyas.12874. Epub 2015 Aug 31. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2015. PMID: 26332952 Review.
-
Negative Influence by the Force: Mechanically Induced Hyperpolarization via K2P Background Potassium Channels.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 23;22(16):9062. doi: 10.3390/ijms22169062. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445768 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Understanding the Cap Structure in K2P Channels.Front Physiol. 2016 Jun 14;7:228. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2016.00228. eCollection 2016. Front Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27378938 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Potassium channel TASK-5 forms functional heterodimers with TASK-1 and TASK-3 to break its silence.Nat Commun. 2024 Aug 30;15(1):7548. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-51288-8. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39215006 Free PMC article.
-
Role of TREK-1 in Health and Disease, Focus on the Central Nervous System.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Apr 11;10:379. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00379. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31031627 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular modulation of TREK-2 activity with nanobodies provides insight into the mechanisms of K2P channel regulation.Nat Commun. 2024 May 16;15(1):4173. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-48536-2. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38755204 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Ion Channel Assembly in a Eukaryotic Cell-Free System Focusing on Two-Pore Domain Potassium Channels K2P.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 27;24(7):6299. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076299. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37047271 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Maingret F, Patel AJ, Lesage F, Lazdunski M, Honoré E. Lysophospholipids open the two-pore domain mechano-gated K(+) channels TREK-1 and TRAAK. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(14):10128–10133. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

