Radical remodeling of the Y chromosome in a recent radiation of malaria mosquitoes
- PMID: 27035980
- PMCID: PMC4839409
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1525164113
Radical remodeling of the Y chromosome in a recent radiation of malaria mosquitoes
Abstract
Y chromosomes control essential male functions in many species, including sex determination and fertility. However, because of obstacles posed by repeat-rich heterochromatin, knowledge of Y chromosome sequences is limited to a handful of model organisms, constraining our understanding of Y biology across the tree of life. Here, we leverage long single-molecule sequencing to determine the content and structure of the nonrecombining Y chromosome of the primary African malaria mosquito, Anopheles gambiae We find that the An. gambiae Y consists almost entirely of a few massively amplified, tandemly arrayed repeats, some of which can recombine with similar repeats on the X chromosome. Sex-specific genome resequencing in a recent species radiation, the An. gambiae complex, revealed rapid sequence turnover within An. gambiae and among species. Exploiting 52 sex-specific An. gambiae RNA-Seq datasets representing all developmental stages, we identified a small repertoire of Y-linked genes that lack X gametologs and are not Y-linked in any other species except An. gambiae, with the notable exception of YG2, a candidate male-determining gene. YG2 is the only gene conserved and exclusive to the Y in all species examined, yet sequence similarity to YG2 is not detectable in the genome of a more distant mosquito relative, suggesting rapid evolution of Y chromosome genes in this highly dynamic genus of malaria vectors. The extensive characterization of the An. gambiae Y provides a long-awaited foundation for studying male mosquito biology, and will inform novel mosquito control strategies based on the manipulation of Y chromosomes.
Keywords: Anopheles gambiae; PacBio; RNA-Seq; Y-chromosome; tandem repetitive DNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

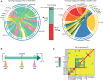
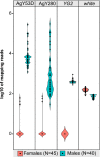

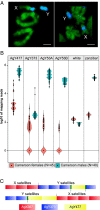
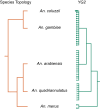
Comment in
-
Genomic Dark Matter Illuminated: Anopheles Y Chromosomes.Trends Parasitol. 2016 Aug;32(8):585-587. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2016.05.008. Epub 2016 Jun 2. Trends Parasitol. 2016. PMID: 27263828
Similar articles
-
Cross-Species Y Chromosome Function Between Malaria Vectors of the Anopheles gambiae Species Complex.Genetics. 2017 Oct;207(2):729-740. doi: 10.1534/genetics.117.300221. Epub 2017 Aug 31. Genetics. 2017. PMID: 28860320 Free PMC article.
-
Genome analysis of a major urban malaria vector mosquito, Anopheles stephensi.Genome Biol. 2014 Sep 23;15(9):459. doi: 10.1186/s13059-014-0459-2. Genome Biol. 2014. PMID: 25244985 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and characterization of Y chromosome sequences from the African malaria mosquito Anopheles gambiae.Genetics. 2004 Mar;166(3):1291-302. doi: 10.1534/genetics.166.3.1291. Genetics. 2004. PMID: 15082548 Free PMC article.
-
Six novel Y chromosome genes in Anopheles mosquitoes discovered by independently sequencing males and females.BMC Genomics. 2013 Apr 23;14:273. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-273. BMC Genomics. 2013. PMID: 23617698 Free PMC article.
-
Site-specific genetic engineering of the Anopheles gambiae Y chromosome.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 May 27;111(21):7600-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1404996111. Epub 2014 May 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 24821795 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A coffee berry borer (Hypothenemus hampei) genome assembly reveals a reduced chemosensory receptor gene repertoire and male-specific genome sequences.Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 1;11(1):4900. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-84068-1. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33649370 Free PMC article.
-
Anopheles gambiae Genome Conservation as a Resource for Rational Gene Drive Target Site Selection.Insects. 2021 Jan 23;12(2):97. doi: 10.3390/insects12020097. Insects. 2021. PMID: 33498790 Free PMC article.
-
A review on the progress of sex-separation techniques for sterile insect technique applications against Anopheles arabiensis.Parasit Vectors. 2018 Dec 24;11(Suppl 2):646. doi: 10.1186/s13071-018-3219-4. Parasit Vectors. 2018. PMID: 30583746 Free PMC article. Review.
-
De novo assembly of a young Drosophila Y chromosome using single-molecule sequencing and chromatin conformation capture.PLoS Biol. 2018 Jul 30;16(7):e2006348. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.2006348. eCollection 2018 Jul. PLoS Biol. 2018. PMID: 30059545 Free PMC article.
-
A perspective on the need and current status of efficient sex separation methods for mosquito genetic control.Parasit Vectors. 2018 Dec 24;11(Suppl 2):654. doi: 10.1186/s13071-018-3222-9. Parasit Vectors. 2018. PMID: 30583720 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bull JJ. The Evolution of Sex Determining Mechanisms. Benjamin/Cummings; Menlo Park, CA: 1983.
-
- Rice WR. Sex chromosomes and the evolution of sexual dimorphism. Evolution. 1984;38(4):735–742. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

