Nociceptin receptor antagonist SB 612111 decreases high fat diet binge eating
- PMID: 27036650
- PMCID: PMC4896639
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbr.2016.03.046
Nociceptin receptor antagonist SB 612111 decreases high fat diet binge eating
Abstract
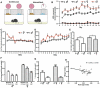
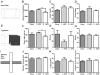
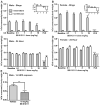
Binge eating is a dysregulated form of feeding behavior that occurs in multiple eating disorders including binge-eating disorder, the most common eating disorder. Feeding is a complex behavioral program supported through the function of multiple brain regions and influenced by a diverse array of receptor signaling pathways. Previous studies have shown the overexpression of the opioid neuropeptide nociceptin (orphanin FQ, N/OFQ) can induce hyperphagia, but the role of endogenous nociceptin receptor (NOP) in naturally occurring palatability-induced hyperphagia is unknown. In this study we adapted a simple, replicable form of binge eating of high fat food (HFD). We found that male and female C57BL/6J mice provided with daily one-hour access sessions to HFD eat significantly more during this period than those provided with continuous 24h access. This form of feeding is rapid and entrained. Chronic intermittent HFD binge eating produced hyperactivity and increased light zone exploration in the open field and light-dark assays respectively. Treatment with the potent and selective NOP antagonist SB 612111 resulted in a significant dose-dependent reduction in binge intake in both male and female mice, and, unlike treatment with the serotonin selective reuptake inhibitor fluoxetine, produced no change in total 24-h food intake. SB 612111 treatment also significantly decreased non-binge-like acute HFD consumption in male mice. These data are consistent with the hypothesis that high fat binge eating is modulated by NOP signaling and that the NOP system may represent a promising novel receptor to explore for the treatment of binge eating.
Keywords: Binge eating; Fluoxetine; High fat; Hyperphagia; Intermittent access; Nociceptin.
Copyright © 2016. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of Nociceptin/Orphanin FQ-NOP Receptor System in the Regulation of Stress-Related Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 30;22(23):12956. doi: 10.3390/ijms222312956. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34884757 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NOP Receptor Antagonists Decrease Alcohol Drinking in the Dark in C57BL/6J Mice.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2019 Oct;43(10):2167-2178. doi: 10.1111/acer.14165. Epub 2019 Aug 21. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2019. PMID: 31386211 Free PMC article.
-
The biology of Nociceptin/Orphanin FQ (N/OFQ) related to obesity, stress, anxiety, mood, and drug dependence.Pharmacol Ther. 2014 Mar;141(3):283-99. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.10.011. Epub 2013 Nov 1. Pharmacol Ther. 2014. PMID: 24189487 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacological characterization of the nociceptin/orphanin FQ receptor antagonist SB-612111 [(-)-cis-1-methyl-7-[[4-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)piperidin-1-yl]methyl]-6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-5H-benzocyclohepten-5-ol]: in vivo studies.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007 Jun;321(3):968-74. doi: 10.1124/jpet.106.116780. Epub 2007 Feb 28. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007. PMID: 17329551
-
A Novel Nociceptin Receptor Antagonist LY2940094 Inhibits Excessive Feeding Behavior in Rodents: A Possible Mechanism for the Treatment of Binge Eating Disorder.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2016 Feb;356(2):493-502. doi: 10.1124/jpet.115.228221. Epub 2015 Dec 9. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2016. PMID: 26659925
Cited by
-
Nociceptin/orphanin FQ neurons in the Arcuate Nucleus and Ventral Tegmental Area Act via Nociceptin Opioid Peptide Receptor Signaling to Inhibit Proopiomelanocortin and A10 Dopamine Neurons and Thereby Modulate Ingestion of Palatable Food.Physiol Behav. 2021 Jan 1;228:113183. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2020.113183. Epub 2020 Sep 23. Physiol Behav. 2021. PMID: 32979341 Free PMC article.
-
The Melanocortin System behind the Dysfunctional Eating Behaviors.Nutrients. 2020 Nov 14;12(11):3502. doi: 10.3390/nu12113502. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 33202557 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Food Addiction and Binge Eating: Lessons Learned from Animal Models.Nutrients. 2018 Jan 11;10(1):71. doi: 10.3390/nu10010071. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 29324652 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Septo-hypothalamic regulation of binge-like alcohol consumption by the nociceptin system.Cell Rep. 2025 Apr 22;44(4):115482. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2025.115482. Epub 2025 Mar 27. Cell Rep. 2025. PMID: 40153436 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Nociceptin/Orphanin FQ-NOP Receptor System in the Regulation of Stress-Related Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 30;22(23):12956. doi: 10.3390/ijms222312956. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34884757 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dingemans AE, Bruna MJ, Van Furth EF. Binge eating disorder: a review. International Journal of Obesity. 2002;26:299–307. - PubMed
-
- Bulik CM, Sullivan PF, Kendler KS. Heritability of binge-eating and broadly defined bulimia nervosa. Bps. 1998;44:1210–8. - PubMed
-
- Bulik CM, Sullivan PF, Kendler KS. Genetic and environmental contributions to obesity and binge eating. Int J Eat Disord. 2003;33:293–8. doi:10.1002/eat.10140. - PubMed
-
- Brownley KA, Berkman ND, Sedway JA, Lohr KN, Bulik CM. Binge eating disorder treatment: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Int J Eat Disord. 2007;40:337–48. doi:10.1002/eat.20370. - PubMed
-
- McElroy SL, Hudson JI, Mitchell JE, Wilfley D, Ferreira-Cornwell MC, Gao J, et al. Efficacy and Safety of Lisdexamfetamine for Treatment of Adults With Moderate to Severe Binge-Eating Disorder. JAMA Psychiatry. 2015;72:235. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2014.2162. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

