Nucleic acids delivery methods for genome editing in zygotes and embryos: the old, the new, and the old-new
- PMID: 27037013
- PMCID: PMC4815204
- DOI: 10.1186/s13062-016-0115-8
Nucleic acids delivery methods for genome editing in zygotes and embryos: the old, the new, and the old-new
Abstract
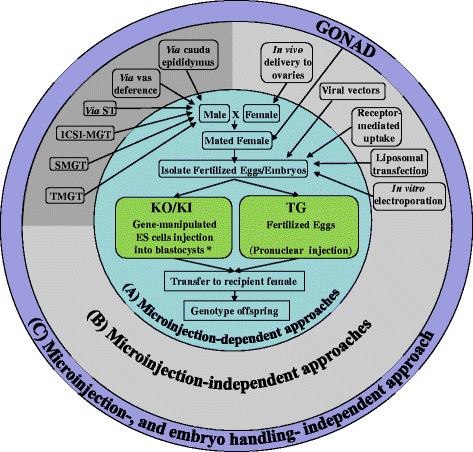
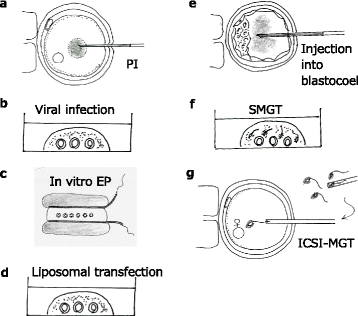
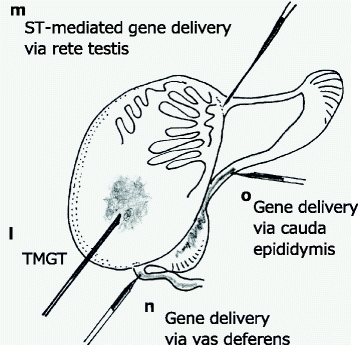
In the recent years, sequence-specific nucleases such as ZFNs, TALENs, and CRISPR/Cas9 have revolutionzed the fields of animal genome editing and transgenesis. However, these new techniques require microinjection to deliver nucleic acids into embryos to generate gene-modified animals. Microinjection is a delicate procedure that requires sophisticated equipment and highly trained and experienced technicians. Though over a dozen alternate approaches for nucleic acid delivery into embryos were attempted during the pre-CRISPR era, none of them became routinely used as microinjection. The addition of CRISPR/Cas9 to the genome editing toolbox has propelled the search for novel delivery approaches that can obviate the need for microinjection. Indeed, some groups have recently developed electroporation-based methods that have the potential to radically change animal transgenesis. This review provides an overview of the old and new delivery methods, and discusses various strategies that were attempted during the last three decades. In addition, several of the methods are re-evaluated with respect to their suitability to deliver genome editing components, particularly CRISPR/Cas9, to embryos.
Keywords: CRISPR/Cas; Genome editing; Mcroinjection; Nucleic acids delivery; Pronuclaer injection; Transgenic.
Figures

Similar articles
-
In vivo genome editing targeted towards the female reproductive system.Arch Pharm Res. 2018 Sep;41(9):898-910. doi: 10.1007/s12272-018-1053-z. Epub 2018 Jul 4. Arch Pharm Res. 2018. PMID: 29974342 Review.
-
Recent Advances in the Production of Genome-Edited Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 25;23(5):2548. doi: 10.3390/ijms23052548. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35269691 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GONAD: A Novel CRISPR/Cas9 Genome Editing Method that Does Not Require Ex Vivo Handling of Embryos.Curr Protoc Hum Genet. 2016 Jan 1;88:15.8.1-15.8.12. doi: 10.1002/0471142905.hg1508s88. Curr Protoc Hum Genet. 2016. PMID: 26724720 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental competence of porcine genome-edited zygotes.Mol Reprod Dev. 2017 Sep;84(9):814-821. doi: 10.1002/mrd.22829. Epub 2017 Jun 8. Mol Reprod Dev. 2017. PMID: 28471514 Review.
-
Electroporation enables the efficient mRNA delivery into the mouse zygotes and facilitates CRISPR/Cas9-based genome editing.Sci Rep. 2015 Jun 11;5:11315. doi: 10.1038/srep11315. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26066060 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Generating mouse models for biomedical research: technological advances.Dis Model Mech. 2019 Jan 8;12(1):dmm029462. doi: 10.1242/dmm.029462. Dis Model Mech. 2019. PMID: 30626588 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bindel-PCR: a novel and convenient method for identifying CRISPR/Cas9-induced biallelic mutants through modified PCR using Thermus aquaticus DNA polymerase.Sci Rep. 2019 Jul 9;9(1):9923. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-46357-8. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31289302 Free PMC article.
-
Triple gene editing in porcine embryos using electroporation alone or in combination with microinjection.Vet World. 2022 Feb;15(2):496-501. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2022.496-501. Epub 2022 Feb 27. Vet World. 2022. PMID: 35400948 Free PMC article.
-
An Overview of the CRISPR-Based Genomic- and Epigenome-Editing System: Function, Applications, and Challenges.Adv Biomed Res. 2019 Aug 21;8:49. doi: 10.4103/abr.abr_41_19. eCollection 2019. Adv Biomed Res. 2019. PMID: 31516887 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Highly Efficient Transgenesis in Ferrets Using CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Homology-Independent Insertion at the ROSA26 Locus.Sci Rep. 2019 Feb 13;9(1):1971. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-37192-4. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30760763 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

