Hyperthyroidism
- PMID: 27038492
- PMCID: PMC5014602
- DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)00278-6
Hyperthyroidism
Abstract
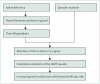
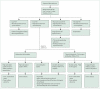
Hyperthyroidism is characterised by increased thyroid hormone synthesis and secretion from the thyroid gland, whereas thyrotoxicosis refers to the clinical syndrome of excess circulating thyroid hormones, irrespective of the source. The most common cause of hyperthyroidism is Graves' disease, followed by toxic nodular goitre. Other important causes of thyrotoxicosis include thyroiditis, iodine-induced and drug-induced thyroid dysfunction, and factitious ingestion of excess thyroid hormones. Treatment options for Graves' disease include antithyroid drugs, radioactive iodine therapy, and surgery, whereas antithyroid drugs are not generally used long term in toxic nodular goitre, because of the high relapse rate of thyrotoxicosis after discontinuation. β blockers are used in symptomatic thyrotoxicosis, and might be the only treatment needed for thyrotoxicosis not caused by excessive production and release of the thyroid hormones. Thyroid storm and hyperthyroidism in pregnancy and during the post-partum period are special circumstances that need careful assessment and treatment.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Hedberg CW, Fishbein DB, Janssen RS, et al. An outbreak of thyrotoxicosis caused by the consumption of bovine thyroid gland in ground beef. N Engl J Med. 1987;316:993–98. - PubMed
-
- Cooper DS, Biondi B. Subclinical thyroid disease. Lancet. 2012;379:1142–54. - PubMed
-
- Garmendia Madariaga A, Santos Palacios S, Guillén-Grima F, Galofré JC. The incidence and prevalence of thyroid dysfunction in Europe: a meta-analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014;99:923–31. - PubMed
-
- Hollowell JG, Staehling NW, Flanders WD, et al. Serum TSH, T(4), and thyroid antibodies in the United States population (1988 to 1994): National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES III) J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002;87:489–99. - PubMed
-
- Vejbjerg P, Knudsen N, Perrild H, et al. Lower prevalence of mild hyperthyroidism related to a higher iodine intake in the population: prospective study of a mandatory iodization programme. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2009;71:440–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

