Inherent physical characteristics and gene expression differences between alveolar and basal bones
- PMID: 27039006
- PMCID: PMC4893923
- DOI: 10.1016/j.oooo.2016.01.008
Inherent physical characteristics and gene expression differences between alveolar and basal bones
Abstract
Objectives: The objective of this study was to evaluate the baseline differences between alveolar and basal areas of the rat mandible.
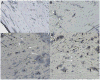
Study design: Rat mandibular alveolar and basal bones were evaluated using histology and micro-computed tomography to compare osteocyte number as well as bone density and architecture and polymerase chain reaction to measure gene expression levels.
Results: Micro-computed tomography data indicated that basal bone is denser and less porous than alveolar bone. Histologic analysis showed that alveolar bone has more osteocytes per unit area compared with basal bone. Real-time polymerase chain reaction results showed higher levels of expression of the following genes in basal bone than in alveolar bone: SOST, E-11, DMP-1, and MEPE.
Conclusions: Three of these gene products are associated with mature osteocytes, and this suggests that basal bone has more mature osteocyte phenotypes compared with alveolar bone. These findings are suggestive of fewer bone mineralization units and therefore a slower remodeling rate.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


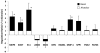
Similar articles
-
Pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) reduced expression and synthesis of SOST/sclerostin in bone explant cultures: implication of PEDF-osteocyte gene regulation in vivo.J Bone Miner Metab. 2019 Sep;37(5):773-779. doi: 10.1007/s00774-018-0982-4. Epub 2019 Jan 3. J Bone Miner Metab. 2019. PMID: 30607618
-
Isolation and culture of primary osteocytes from the long bones of skeletally mature and aged mice.Biotechniques. 2012 Jun;52(6):361-73. doi: 10.2144/0000113876. Biotechniques. 2012. PMID: 22668415 Free PMC article.
-
Sclerostin and DKK1 Inhibition Preserves and Augments Alveolar Bone Volume and Architecture in Rats with Alveolar Bone Loss.J Dent Res. 2018 Aug;97(9):1031-1038. doi: 10.1177/0022034518766874. Epub 2018 Apr 4. J Dent Res. 2018. PMID: 29617179
-
Bone mineralization is regulated by signaling cross talk between molecular factors of local and systemic origin: the role of fibroblast growth factor 23.Biofactors. 2014 Nov-Dec;40(6):555-68. doi: 10.1002/biof.1186. Epub 2014 Oct 29. Biofactors. 2014. PMID: 25352227 Review.
-
The osteocyte lineage.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2008 May 15;473(2):106-11. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2008.04.009. Epub 2008 Apr 18. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2008. PMID: 18424256 Review.
Cited by
-
Calcium‑dependent activation of PHEX, MEPE and DMP1 in osteocytes.Mol Med Rep. 2022 Dec;26(6):359. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2022.12876. Epub 2022 Oct 25. Mol Med Rep. 2022. PMID: 36281920 Free PMC article.
-
Tooth-Supporting Hard Tissue Regeneration Using Biopolymeric Material Fabrication Strategies.Molecules. 2020 Oct 19;25(20):4802. doi: 10.3390/molecules25204802. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33086674 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hildebolt CF. Osteoporosis and oral bone loss. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 1997;26:3–15. - PubMed
-
- Manzke E, Chesnut CH, 3rd, Wergedal JE, Baylink DJ, Nelp WB. Relationship between local and total bone mass in osteoporosis. Metabolism. 1975;24:605–615. - PubMed
-
- Bertoldo F, Santini D, Lo Cascio V. Bisphosphonates and osteomyelitis of the jaw: a pathogenic puzzle. Nat Clin Pract Oncol. 2007;4:711–721. - PubMed
-
- Klemetti E, Kolmakov S, Heiskanen P, Vainio P, Lassila V. Panoramic mandibular index and bone mineral densities in post-menopausal women. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1993;75:774–779. - PubMed
-
- Kato Y, Windle JJ, Koop BA, Mundy GR, Bonewald LF. Establishment of an osteocyte-like cell line, MLO-Y4. J Bone Miner Res. 1997;12:2014–2023. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

