Rapid chondrolysis of the medial knee compartment after arthroscopic meniscal resection: a case report
- PMID: 27039072
- PMCID: PMC4818872
- DOI: 10.1186/s13256-016-0841-7
Rapid chondrolysis of the medial knee compartment after arthroscopic meniscal resection: a case report
Abstract
Background: Rapidly destructive osteoarthritis of the hip and rapid chondrolysis of the lateral compartment of the knee or the shoulder are rare, but have been previously described in the medical literature. To the best of our knowledge, no case of medial femorotibial compartment chondrolysis after arthroscopy has yet been described. We therefore submit the first case report.
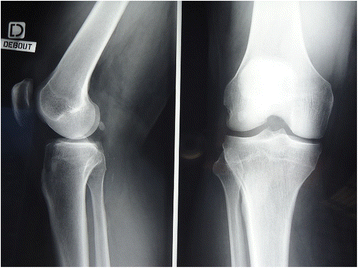
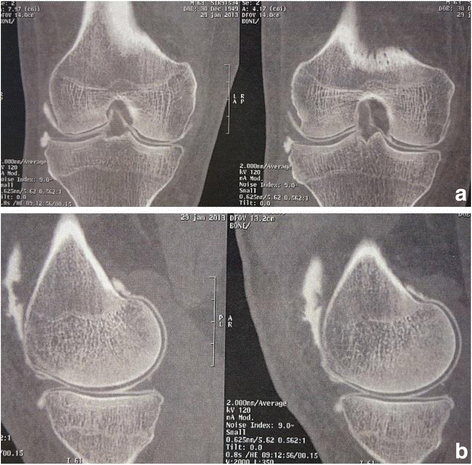
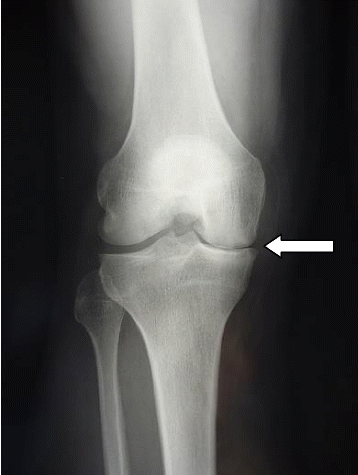
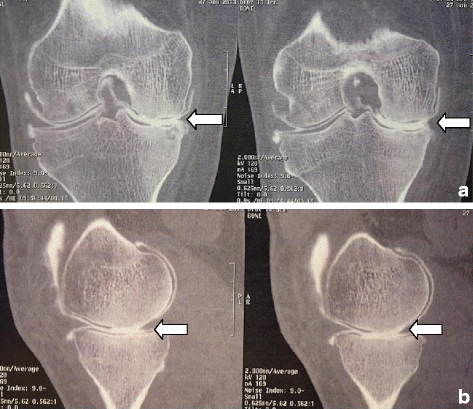
Case presentation: A 64-year-old white European man presented with right knee pain due to a medial meniscal tear with no other abnormality found on examination or imaging. An arthroscopic partial medial meniscectomy was performed and early evolution was favorable with no signs of infection. He developed knee pain 2 months later. X-rays showed a thinning of the medial compartment which was confirmed by computed tomography arthrogram. There was no articular effusion, mobility was conserved (0/0/125°), there was no laxity, and pain was localized to the medial femorotibial compartment, with no meniscal signs. There was a 8° varus deviation (versus 3° for his uninjured left knee). His blood work was normal. As there were no signs of infection, no aspiration was performed. Viscosupplementation was offered but refused by the patient. He is now waiting for a partial knee replacement.
Conclusions: To the best of our knowledge, this is the first description of such a case. Rapid chondrolysis has been described in the hip, shoulder, and the lateral compartment of the knee. Infiltration of bupivacaine and lateral meniscectomy are the most frequently sited offending procedures. Concerning the medial compartment, cases of avascular necrosis have been reported after meniscectomy or use of radiofrequency devices. This case underlines the necessity of a thorough physical examination and complete radiological work up before any surgery. It must also drive us to use caution regarding meniscectomy, especially in patients over 60 years of age, and reminds us that patients must be informed of this potential complication.
Keywords: Arthroscopy; Case report; Complication; Knee; Rapid chondrolysis.
Figures
References
-
- Coobs BR, LaPrade RF. Severe chondrolysis of the glenohumeral joint after shoulder thermal capsulorrhaphy. Am J Orthop. 2009;38:E34–7. - PubMed
-
- Douw CM, Bulstra SK, Vandenbroucke J, Geesink RG, Vermeulen A. Clinical and pathological changes in the knee after accidental chlorhexidine irrigation during arthroscopy: case reports and review of the literature. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1998;80:437–40. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.80B3.8519. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

