Changes in lipoprotein lipase and endothelial lipase mass in familial hypercholesterolemia during three-drug lipid-lowering combination therapy
- PMID: 27039080
- PMCID: PMC4818918
- DOI: 10.1186/s12944-016-0238-z
Changes in lipoprotein lipase and endothelial lipase mass in familial hypercholesterolemia during three-drug lipid-lowering combination therapy
Abstract
Background: This study was performed to compare the effects of three different lipid-lowering therapies (statins, ezetimibe, and colestimide) on lipoprotein lipase and endothelial lipase masses in pre-heparin plasma (pre-heparin LPL and EL mass, respectively) from patients with familial hypercholesterolemia (FH). FH is usually treated by coadministration of these three drugs.
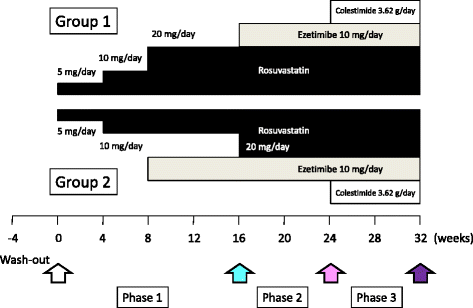
Methods: The pre-heparin LPL and EL masses were measured in fresh frozen plasma drawn and stored at various time points during coadministration of the three drugs from patients with heterozygous FH harboring a single mutation in the LDL receptor (n = 16, mean age 63 years). The patients were randomly divided into two groups based on the timing when ezetimibe was added.
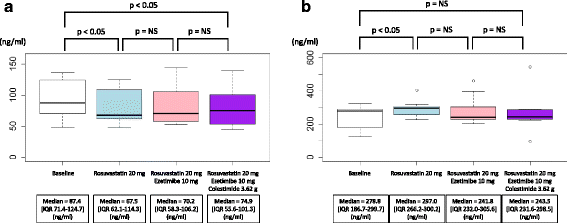
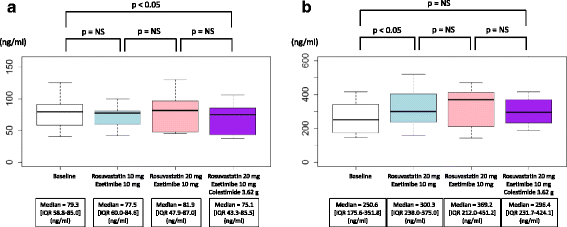
Results: Plasma LPL mass concentration was significantly reduced by rosuvastatin at 20 mg/day (median = 87.4 [IQR: 71.4-124.7] to 67.5 [IQR: 62.1-114.3] ng/ml, P < 0.05). In contrast, ezetimibe at 10 mg/day as well as colestimide at 3.62 g/day did not alter its level substantially (median = 67.5 [IQR: 62.1-114.3] to 70.2 [IQR: 58.3-106.2], and to 74.9 [IQR: 55.6-101.3] ng/ml, respectively) in the group starting with rosuvastatin followed by the addition of ezetimibe and colestimide. On the other hand, the magnitude in LPL mass reduction was lower in the group starting with ezetimibe at 10 mg/day before reaching the maximum dose of 20 mg/day of rosuvastatin. Plasma EL mass concentration was significantly increased by rosuvastatin at 20 mg/day (median = 278.8 [IQR: 186.7-288.7] to 297.0 [IQR: 266.2-300.2] ng/ml, P < 0.05), whereas other drugs did not significantly alter its level.
Conclusion: The effects on changes of LPL and EL mass differed depending on the lipid-lowering therapy, which may impact the prevention of atherosclerosis differently.
Keywords: Endothelial lipase; Familial hypercholesterolemia; Lipoprotein lipase.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of coadministration of rosuvastatin, ezetimibe, and colestimide in heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia.Am J Cardiol. 2012 Feb 1;109(3):364-9. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2011.09.019. Epub 2011 Nov 22. Am J Cardiol. 2012. PMID: 22112743 Clinical Trial.
-
Attainment of LDL-Cholesterol Treatment Goals in Patients With Familial Hypercholesterolemia: 5-Year SAFEHEART Registry Follow-Up.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016 Mar 22;67(11):1278-85. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2016.01.008. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016. PMID: 26988947
-
Efficacy of colestimide coadministered with atorvastatin in japanese patients with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (FH).Circ J. 2005 May;69(5):515-20. doi: 10.1253/circj.69.515. Circ J. 2005. PMID: 15849435 Clinical Trial.
-
Type of LDLR mutation and the pharmacogenetics of familial hypercholesterolemia treatment.Pharmacogenomics. 2015;16(15):1743-50. doi: 10.2217/pgs.15.113. Epub 2015 Oct 2. Pharmacogenomics. 2015. PMID: 26427613 Review.
-
The efficacy of colesevelam HCl in the treatment of heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia in pediatric and adult patients.Clin Ther. 2013 Aug;35(8):1247-52. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2013.06.014. Epub 2013 Jul 31. Clin Ther. 2013. PMID: 23916045 Review.
Cited by
-
Serum Triglyceride Lipase Concentrations are Independent Risk Factors for Coronary Artery Disease and In-Stent Restenosis.J Atheroscler Thromb. 2019 Sep 1;26(9):762-774. doi: 10.5551/jat.46821. Epub 2019 Jan 17. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2019. PMID: 30651409 Free PMC article.
-
Which is the Best Predictor for the Development of Atherosclerosis Among Circulating Lipoprotein Lipase, Hepatic Lipase, and Endothelial Lipase?J Atheroscler Thromb. 2019 Sep 1;26(9):758-759. doi: 10.5551/jat.ED108. Epub 2019 Feb 27. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2019. PMID: 30814386 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Statins for children with familial hypercholesterolemia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jul 7;7(7):CD006401. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006401.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Nov 7;2019(11). doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006401.pub5. PMID: 28685504 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Statins for children with familial hypercholesterolemia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Nov 7;2019(11):CD006401. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006401.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31696945 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

