Oral immunoglobulin for preventing necrotizing enterocolitis in preterm and low birth weight neonates
- PMID: 27040323
- PMCID: PMC6464658
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD001816.pub3
Oral immunoglobulin for preventing necrotizing enterocolitis in preterm and low birth weight neonates
Abstract
Background: Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) is the most common emergency involving the gastrointestinal tract occurring in the neonatal period. There have been published reports that suggest that oral immunoglobulins (Ig)A and IgG produce an immunoprotective effect in the gastrointestinal mucosa.
Objectives: To determine the effect of oral immunoglobulin on the incidence of necrotizing enterocolitis and other complications in preterm or low birth weight (or both) neonates.
Search methods: We used the standard search strategy of the Cochrane Neonatal Group. We searched the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL, The Cochrane Library 2016, Issue 1), PubMed (1966 to January 2016), CINAHL (1982 to January 2016) and EMBASE (1980 to January 2016) and conference proceedings.
Selection criteria: All randomized or quasi-randomised controlled trials where oral immunoglobulins were used as prophylaxis against NEC in preterm (less than 37 weeks' gestation) or low birth weight (less than 2500 gram), or both, neonates.
Data collection and analysis: We performed data collection and analysis in accordance with the standard methods of the Cochrane Neonatal Review Group.
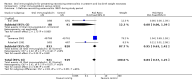
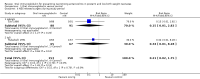
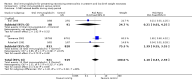
Main results: The search identified five studies on oral immunoglobulin for the prevention of NEC of which three met the inclusion criteria. In this review of the three eligible trials (including 2095 neonates), the oral administration of IgG or an IgG/IgA combination did not result in a significant reduction in the incidence of definite NEC (typical risk ratio (RR) 0.84, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.57 to 1.25; typical risk difference (RD) -0.01, 95% CI -0.03 to 0.01; 3 studies, 1840 infants), suspected NEC (RR 0.84, 95% CI 0.49 to 1.46; RD -0.01, 95% CI -0.02 to 0.01; 1 study, 1529 infants), need for surgery (typical RR 0.21, 95% CI 0.02 to 1.75; typical RD -0.03, 95% CI -0.06 to 0.00; 2 studies, 311 infants) or death from NEC (typical RR 1.10, 95% CI 0.47 to 2.59; typical RD 0.00, 95% CI -0.01 to 0.01; 3 studies, 1840 infants).
Authors' conclusions: Based on the available trials, the evidence does not support the administration of oral immunoglobulin for the prevention of NEC. There are no randomized controlled trials of oral IgA alone for the prevention of NEC.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

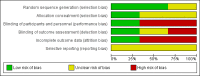




Update of
-
Oral immunoglobulin for preventing necrotizing enterocolitis in preterm and low birth-weight neonates.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004;(1):CD001816. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001816.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Apr 04;4:CD001816. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001816.pub3. PMID: 14973972 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Eibl 1988 {published data only}
-
- Eibl MM, Wolf HM, Furnkranz H, Rosenkranz A. Prevention of necrotizing enterocolitis in low‐birth‐weight infants by IgA‐IgG feeding. New England Journal of Medicine 1988;319(1):1‐7. [PUBMED: 3288866] - PubMed
Lawrence 2001 {published data only}
-
- Lawrence G, Tudehope D, Baumann K, Jeffery H, Gill A, Cole M, et al. Enteral human IgG for prevention of necrotising enterocolitis: a placebo‐controlled, randomised trial. Lancet 2001;357(9274):2090‐4. [PUBMED: 11445103] - PubMed
-
- Lawrence GW, The Australian NEC Study Group, Baumann K, Swanson C. Controlled double blind trial of oral human IgG in preventing neonatal enterocolitis (NEC). Proceedings of the Australian New Zealand Perinatal Society. 1996:A80.
Rubaltelli 1991 {published data only}
-
- Rubaltelli FF, Benini F, Sala M. Prevention of necrotizing enterocolitis in neonates at risk by oral administration of monomeric IgG. Developmental Pharmacology and Therapeutics 1991;17(3‐4):138‐43. [PUBMED: 1841829] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Fast 1994 {published data only}
-
- Fast C, Rosegger H. Necrotizing enterocolitis prophylaxis: oral antibiotics and lyophilized enterobacteria vs oral immunoglobulins. Acta Paediatrica. Supplement 1994;396:86‐90. [PUBMED: 8086694] - PubMed
Richter 1998 {published data only}
-
- Richter D, Bartmann P, Pohlandt F. Prevention of necrotizing enterocolitis in extremely low birth weight infants by IgG feeding?. European Journal of Pediatrics 1998;157(11):924‐5. [PUBMED: 9835438] - PubMed
Additional references
Attaelmannan 2000
-
- Attaelmannan M, Levinson SS. Understanding and identifying monoclonal gammopathies. Clinical Chemistry 2000;46(8 Pt 2):1230‐8. [PUBMED: 10926917] - PubMed
Bauer 1992
-
- Bauer CR. Necrotizing enterocolitis. In: Sinclair JC, Bracken MB editor(s). Effective Care of the Newborn Infant. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1992.
Cikrit 1984
-
- Cikrit D, Mastandrea J, West KW, Schreiner RL, Grosfeld JL. Necrotizing enterocolitis: factors affecting mortality in 101 surgical cases. Surgery 1984;96(4):648‐55. [PUBMED: 6484808] - PubMed
Claud 2009
Cotten 2009
-
- Cotten CM, Taylor S, Stoll B, Goldberg RN, Hansen NI, Sánchez PJ, et al. Prolonged duration of initial empirical antibiotic treatment is associated with increased rates of necrotizing enterocolitis and death for extremely low birth weight infants. Pediatrics 2009;123(1):58‐66. [PUBMED: 19117861] - PMC - PubMed
Edelstone 1982
-
- Edelstone DI, Holzman IR. Fetal intestinal oxygen consumption at various levels of oxygenation. American Journal of Physiology 1982;242(1):H50‐4. [PUBMED: 7058913] - PubMed
Fitzgibbons 2009
-
- Fitzgibbons SC, Ching Y, Yu D, Carpenter J, Kenny M, Weldon C, et al. Mortality of necrotizing enterocolitis expressed by birth weight categories. Journal of Pediatric Surgery 2009;44(6):1072‐5. [PUBMED: 19524719] - PubMed
GRADEpro 2008 [Computer program]
-
- Brozek J, Oxman A, Schünemann H. GRADEpro [Version 3.2 for Windows]. The GRADE Working Group, 2008.
Grylack 1978
-
- Grylack LJ, Scanlon JW. Oral gentamicin therapy in the prevention of neonatal necrotising enterocolitis. A controlled double blind trial. American Journal of Diseases in Childhood 1978;132(12):1192‐4. [PUBMED: 362900] - PubMed
Guyatt 2011a
-
- Guyatt G, Oxman AD, Akl EA, Kunz R, Vist G, Brozek J, et al. GRADE guidelines: 1. Introduction‐GRADE evidence profiles and summary of findings tables. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011;64(4):383‐94. [PUBMED: 21195583] - PubMed
Guyatt 2011b
-
- Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Vist G, Kunz R, Brozek J, Alonso‐Coello P, et al. GRADE guidelines: 4. Rating the quality of evidence‐‐study limitations (risk of bias). Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011;64(4):407‐15. [PUBMED: 21247734] - PubMed
Guyatt 2011c
-
- Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Kunz R, Brozek J, Alonso‐Coello P, Rind D, et al. GRADE guidelines 6. Rating the quality of evidence‐‐imprecision. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011;64(12):1283‐93. [PUBMED: 21839614] - PubMed
Guyatt 2011d
-
- Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Kunz R, Woodcock J, Brozek J, Helfand M, et al. GRADE guidelines: 7. Rating the quality of evidence‐‐inconsistency. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011;64(12):1294‐302. [PUBMED: 21803546] - PubMed
Guyatt 2011e
-
- Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Kunz R, Woodcock J, Brozek J, Helfand M, et al. GRADE guidelines: 8. Rating the quality of evidence‐‐indirectness. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011;64(12):1303‐10. [PUBMED: 21802903] - PubMed
Henry 2009
-
- Henry MC, Moss RL. Necrotizing enterocolitis. Annual Review of Medicine 2009;60:111‐24. [PUBMED: 18817461] - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Hintz 2005
-
- Hintz SR, Kendrick DE, Stoll BJ, Vohr BR, Fanaroff AA, Donovan EF, et al. Neurodevelopmental and growth outcomes of extremely low birth weight infants after necrotizing enterocolitis. Pediatrics 2005;115(3):696‐703. [PUBMED: 15741374] - PubMed
Hseuh 2003
Jacobs 2013
-
- Jacobs SE, Tobin JM, Opie GF, Donath S, Tabrizi SN, Pirotta M, et al. ProPrems Study Group. Probiotic effects on late‐onset sepsis in very preterm infants: a randomized controlled trial. Pediatrics 2013;132(6):1055‐62. [PUBMED: 24249817] - PubMed
Jantscher‐Krenn 2012
Lin 2005
-
- Lin HC, Su BH, Chen AC, Lin TW, Tsai CH, Yeh TF, et al. Oral probiotics reduce the incidence and severity of necrotising enterocolitis in very low birth weight infants. Pediatrics 2005;115(1):1‐4. [PUBMED: 15629973] - PubMed
Lin 2006
-
- Lin PW, Stoll BJ. Necrotising enterocolitis. Lancet 2006;368(9543):1271‐83. [PUBMED: 17027734] - PubMed
Lucas 1990
-
- Lucas A, Cole TJ. Breast milk and neonatal necrotising enterocolitis. Lancet 1990;336(8730):1519‐23. [PUBMED: 1979363] - PubMed
Luig 2005
-
- Luig M, Lui K, NSW & ACT NICUS Group. Epidemiology of necrotizing enterocolitis ‐ part I: changing regional trends in extremely preterm infants over 14 years. Journal of Paediatrics and Child Health 2005;41(4):169‐73. [PUBMED: 15813869] - PubMed
Maheshwari 2011
-
- Maheshwari A, Corbin LL, Schelonka RL. Neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. Research and Reports in Neonatology 2011;1:39‐53.
Martin 2010
Mitchell 2014
Neu 2011
Neu 2012
-
- Neu J, Mihatsch W. Recent developments in necrotizing enterocolitis. Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 2012;36(1 Suppl):30S‐5S. [PUBMED: 22237874] - PubMed
Patole 2007
-
- Patole S. Prevention and treatment of necrotising enterocolitis in preterm neonates. Early Human Development 2007;83(10):635‐42. [PUBMED: 17826009] - PubMed
Petrosyan 2009
-
- Petrosyan M, Guner YS, Williams M, Grishin A, Ford HR. Current concepts regarding the pathogenesis of necrotizing enterocolitis. Pediatric Surgery International 2009;25(4):309‐18. [PUBMED: 19301015] - PubMed
RevMan 2012 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2012.
Schunemann 2013
-
- Schunemann H, Brozek J, Guyatt G, Oxman A, editors. GRADE Working Group. GRADE handbook for grading quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. Available from www.guidelinedevelopment.org/handbook Updated October 2013.
Simon 1994
-
- Simon NP. Follow‐up for infants with necrotizing enterocolitis. Clinics in Perinatology 1994;21(2):411‐24. [PUBMED: 8070234] - PubMed
Stoll 1994a
Stoll 1994b
Stoll 2010
-
- Stoll BJ, Hansen NI, Bell EF, Shankaran S, Laptook AR, Walsh MC, et al. Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Neonatal Research Network. Neonatal outcomes of extremely preterm infants from the NICHD Neonatal Research Network. Pediatrics 2010;126(3):443‐56. [PUBMED: 20732945] - PMC - PubMed
Tudehope 2005
-
- Tudehope DI. The epidemiology and pathogenesis of neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. Journal of Paediatric and Child Health 2005;41(4):167‐8. [PUBMED: 15813868] - PubMed
Willoughby 1994
Wolf 1994
-
- Wolf HM, Eibl MM. The anti‐inflammatory effect of an immunoglobulin (IgA‐IgG) preparation and its possible relevance for the prevention of necrotizing enterocolitis. Acta Paediatrica 1994;396 Suppl:37‐40. [PUBMED: 8086680] - PubMed
Yee 2012
-
- Yee WH, Soraisham AS, Shah VS, Aziz K, Yoon W, Lee SK, Canadian Neonatal Network. Incidence and timing of presentation of necrotizing enterocolitis in preterm infants. Pediatrics 2012;129(2):e298. [PUBMED: 22271701] - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Foster 2001
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

