Splitsville: structural and functional insights into the dynamic bacterial Z ring
- PMID: 27040757
- PMCID: PMC5290750
- DOI: 10.1038/nrmicro.2016.26
Splitsville: structural and functional insights into the dynamic bacterial Z ring
Abstract
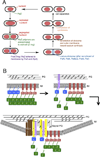
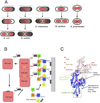
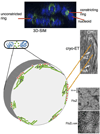
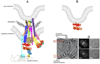
Bacteria must divide to increase in number and colonize their niche. Binary fission is the most widespread means of bacterial cell division, but even this relatively simple mechanism has many variations on a theme. In most bacteria, the tubulin homologue FtsZ assembles into a ring structure, termed the Z ring, at the site of cytokinesis and recruits additional proteins to form a large protein machine - the divisome - that spans the membrane. In this Review, we discuss current insights into the regulation of the assembly of the Z ring and how the divisome drives membrane invagination and septal cell wall growth while flexibly responding to various cellular inputs.
Figures

References
-
- Egan AJ, Vollmer W. The physiology of bacterial cell division. Ann NY Acad Sci. 2013;1277:8–28. - PubMed
-
- Margolin W. Themes and variations in prokaryotic cell division. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2000;24:531–548. - PubMed
-
- Leisch N, et al. Growth in width and FtsZ ring longitudinal positioning in a gammaproteobacterial symbiont. Curr Biol. 2012;22:R831–R832. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

