Molecular Mechanisms of Neurodegeneration in Spinal Muscular Atrophy
- PMID: 27042141
- PMCID: PMC4807884
- DOI: 10.4137/JEN.S33122
Molecular Mechanisms of Neurodegeneration in Spinal Muscular Atrophy
Abstract
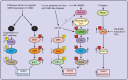
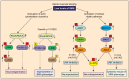
Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is an autosomal recessive motor neuron disease with a high incidence and is the most common genetic cause of infant mortality. SMA is primarily characterized by degeneration of the spinal motor neurons that leads to skeletal muscle atrophy followed by symmetric limb paralysis, respiratory failure, and death. In humans, mutation of the Survival Motor Neuron 1 (SMN1) gene shifts the load of expression of SMN protein to the SMN2 gene that produces low levels of full-length SMN protein because of alternative splicing, which are sufficient for embryonic development and survival but result in SMA. The molecular mechanisms of the (a) regulation of SMN gene expression and (b) degeneration of motor neurons caused by low levels of SMN are unclear. However, some progress has been made in recent years that have provided new insights into understanding of the cellular and molecular basis of SMA pathogenesis. In this review, we have briefly summarized recent advances toward understanding of the molecular mechanisms of regulation of SMN levels and signaling mechanisms that mediate neurodegeneration in SMA.
Keywords: JNK; MND; ROCK; SMA; SMN; ZPR1.
Figures
References
-
- Lefebvre S, Burglen L, Reboullet S, et al. Identification and characterization of a spinal muscular atrophy-determining gene. Cell. 1995;80:155–165. - PubMed
-
- Monani UR, Lorson CL, Parsons DW, et al. A single nucleotide difference that alters splicing patterns distinguishes the SMA gene SMN1 from the copy gene SMN2. Hum Mol Genet. 1999;8:1177–1183. - PubMed
-
- Cusco I, Barcelo MJ, Rojas-Garcia R, et al. SMN2 copy number predicts acute or chronic spinal muscular atrophy but does not account for intrafamilial variability in siblings. J Neurol. 2006;253:21–25. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

