Production of medium-chain fatty acids and higher alcohols by a synthetic co-culture grown on carbon monoxide or syngas
- PMID: 27042211
- PMCID: PMC4818930
- DOI: 10.1186/s13068-016-0495-0
Production of medium-chain fatty acids and higher alcohols by a synthetic co-culture grown on carbon monoxide or syngas
Abstract
Background: Synthesis gas, a mixture of CO, H2, and CO2, is a promising renewable feedstock for bio-based production of organic chemicals. Production of medium-chain fatty acids can be performed via chain elongation, utilizing acetate and ethanol as main substrates. Acetate and ethanol are main products of syngas fermentation by acetogens. Therefore, syngas can be indirectly used as a substrate for the chain elongation process.
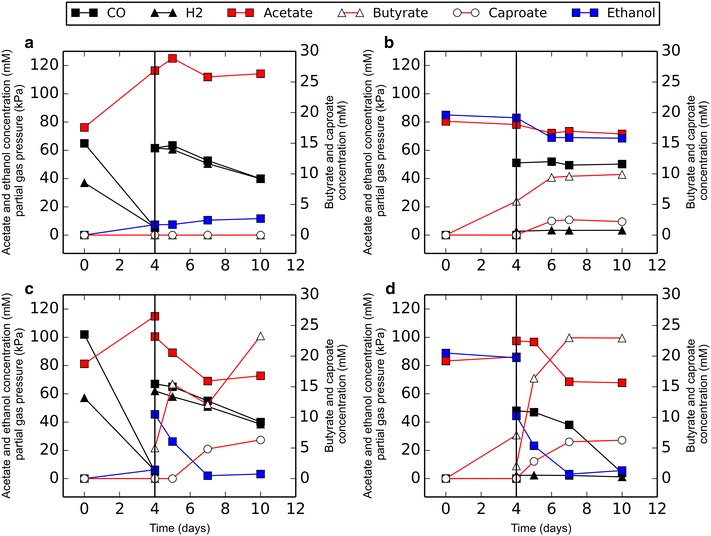
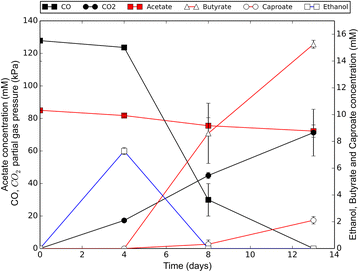
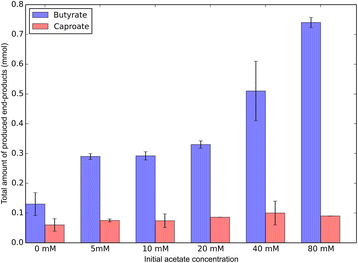
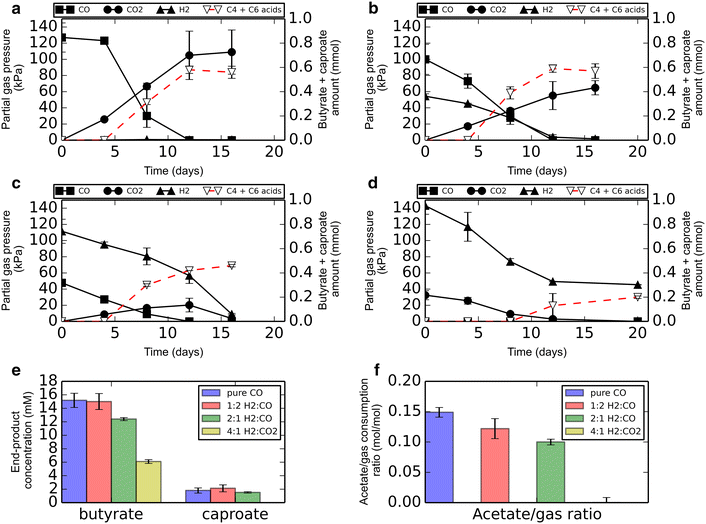
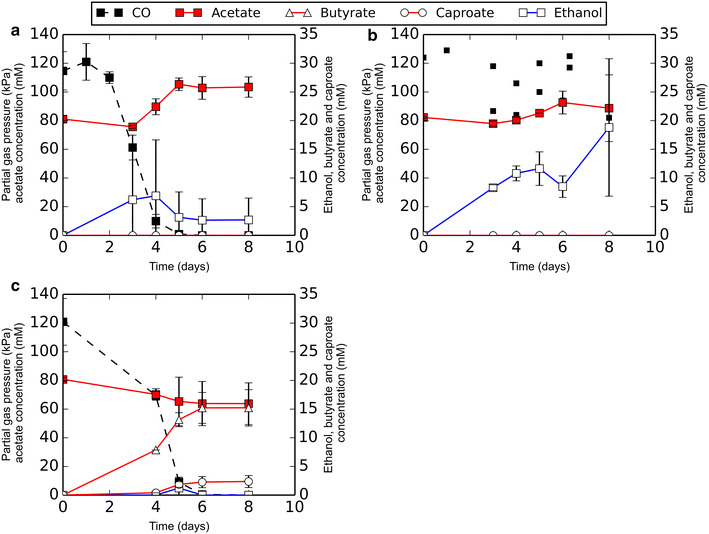
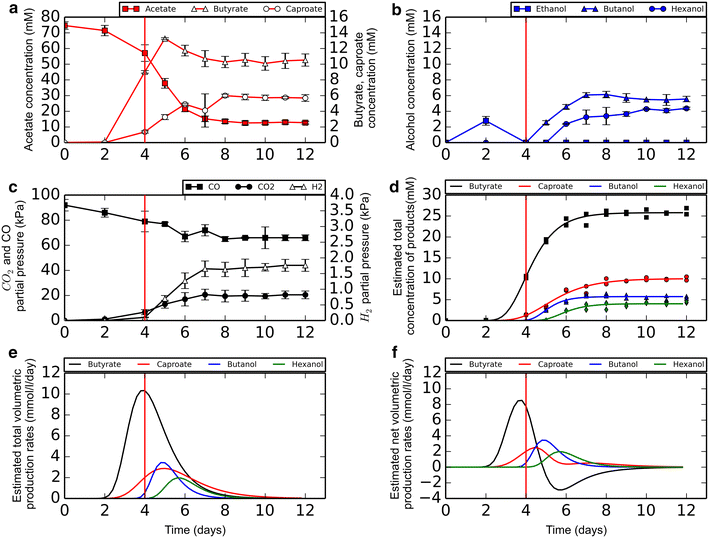
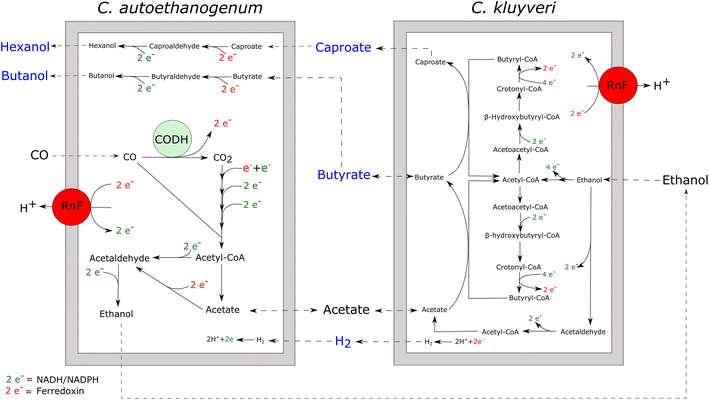
Results: Here, we report the establishment of a synthetic co-culture consisting of Clostridium autoethanogenum and Clostridium kluyveri. Together, these bacteria are capable of converting CO and syngas to a mixture of C4 and C6 fatty acids and their respective alcohols. The co-culture is able to grow using solely CO or syngas as a substrate, and presence of acetate significantly stimulated production rates. The co-culture produced butyrate and caproate at a rate of 8.5 ± 1.1 and 2.5 ± 0.63 mmol/l/day, respectively. Butanol and hexanol were produced at a rate of 3.5 ± 0.69 and 2.0 ± 0.46 mmol/l/day, respectively. The pH was found to be a major factor during cultivation, influencing the growth performance of the separate strains and caproate toxicity.
Conclusion: This co-culture poses an alternative way to produce medium-chain fatty acids and higher alcohols from carbon monoxide or syngas and the process can be regarded as an integration of syngas fermentation and chain elongation in one growth vessel.
Keywords: Butanol; Butyrate; Caproate; Clostridium autoethanogenum; Clostridium kluyveri; Hexanol; Hydrogen.
Figures
References
-
- Frost LJ, Hartvigsen J, Elangovan S. Formation of synthesis gas using solar concentrator photovoltaics (SCPV) and high temperature co-electrolysis (HTCE) of CO2 and H2O. Offshore Technol Conf. 2010
-
- Jeong J, Bertsch J, Hess V, Choi S, Choi IG, Chang IS, Müller V. A model for energy conservation based on genomic and experimental analyses in a carbon monoxide-utilizing, butyrate-forming acetogen, Eubacterium limosum KIST612. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2015;81:4782–4790. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00675-15. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Worden R, Grethlein A, Zeikus J, Datta R. Butyrate production from carbon monoxide by Butyribacterium methylotrophicum. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 1989;20:687–698. doi: 10.1007/BF02936517. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

