Alzheimer Disease
- PMID: 27042902
- PMCID: PMC5390933
- DOI: 10.1212/CON.0000000000000307
Alzheimer Disease
Abstract
Purpose of review: This article discusses the recent advances in the diagnosis and treatment of Alzheimer disease (AD).
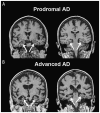
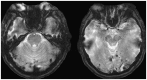
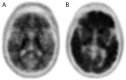
Recent findings: In recent years, significant advances have been made in the fields of genetics, neuroimaging, clinical diagnosis, and staging of AD. One of the most important recent advances in AD is our ability to visualize amyloid pathology in the living human brain. The newly revised criteria for diagnosis of AD dementia embrace the use for biomarkers as supportive evidence for the underlying pathology. Guidelines for the responsible use of amyloid positron emission tomography (PET) have been developed, and the clinical and economic implications of amyloid PET imaging are actively being explored.
Summary: Our improved understanding of the clinical onset, progression, neuroimaging, pathologic features, genetics, and other risk factors for AD impacts the approaches to clinical diagnosis and future therapeutic interventions.
Figures

References
-
- Alzheimer’s Association. 2015. Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement 2015; 11(3): 322– 384. - PubMed
-
- Villemagne VL, Burnham S, Bourgeat P, et al. Amyloid β deposition, neurodegeneration, and cognitive decline in sporadic Alzheimer’s disease: a prospective cohort study. Lancet Neurol 2013; 12(4): 357– 367. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(13)70044-9. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. World atlas of ageing. Kobe, Japan: World Health Organization, Centre for Health Development, 1998.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
