Analysis of a Spontaneous Non-Motile and Avirulent Mutant Shows That FliM Is Required for Full Endoflagella Assembly in Leptospira interrogans
- PMID: 27044038
- PMCID: PMC4820103
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0152916
Analysis of a Spontaneous Non-Motile and Avirulent Mutant Shows That FliM Is Required for Full Endoflagella Assembly in Leptospira interrogans
Abstract
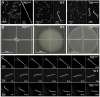
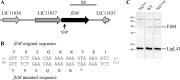
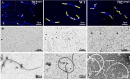
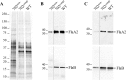
Pathogenic Leptospira strains are responsible for leptospirosis, a worldwide emerging zoonotic disease. These spirochetes are unique amongst bacteria because of their corkscrew-like cell morphology and their periplasmic flagella. Motility is reported as an important virulence determinant, probably favoring entry and dissemination of pathogenic Leptospira in the host. However, proteins constituting the periplasmic flagella and their role in cell shape, motility and virulence remain poorly described. In this study, we characterized a spontaneous L. interrogans mutant strain lacking motility, correlated with the loss of the characteristic hook-shaped ends, and virulence in the animal model. Whole genome sequencing allowed the identification of one nucleotide deletion in the fliM gene resulting in a premature stop codon, thereby preventing the production of flagellar motor switch protein FliM. Genetic complementation restored cell morphology, motility and virulence comparable to those of wild type cells. Analyses of purified periplasmic flagella revealed a defect in flagella assembly, resulting in shortened flagella compared to the wild type strain. This also correlated with a lower amount of major filament proteins FlaA and FlaB. Altogether, these findings demonstrate that FliM is required for full and correct assembly of the flagella which is essential for motility and virulence.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Adler B. History of Leptospirosis and Leptospira In: Adler B, editor. Leptospira and Leptospirosis. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin; Heidelberg; 2015. p. 1–9.
-
- Charon NW, Goldstein SF. Genetics of motility and chemotaxis of a fascinating group of bacteria: the Spirochetes. Annu Rev Genet. 2002. December;36(1):47–73. - PubMed
-
- McBride AJA, Athanazio DA, Reis MG, Ko AI. Leptospirosis. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2005. October;18(5):376–86. - PubMed
-
- Li C, Motaleb A, Sal M, Goldstein SF, Charon NW. Spirochete periplasmic flagella and motility. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2000;2(4):345–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

