Clinical relevance of the tumor microenvironment and immune escape of oral squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 27044404
- PMCID: PMC4820994
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-016-0828-6
Clinical relevance of the tumor microenvironment and immune escape of oral squamous cell carcinoma
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Clinical relevance of the tumor microenvironment and immune escape of oral squamous cell carcinoma.J Transl Med. 2018 Feb 28;16(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s12967-018-1407-9. J Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 29486780 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Changes in the tumor microenvironment and immune surveillance represent crucial hallmarks of various kinds of cancer, including oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC), and a close crosstalk of hypoxia regulating genes, an activation of chemokines and immune cells has been described.
Methods: A review about the pivotal role of HIF-1, its crosstalk to various cornerstones in OSCC tumorigenesis is presented.
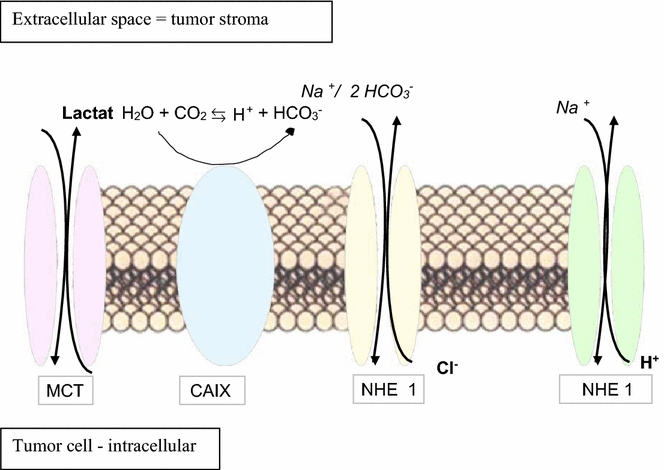
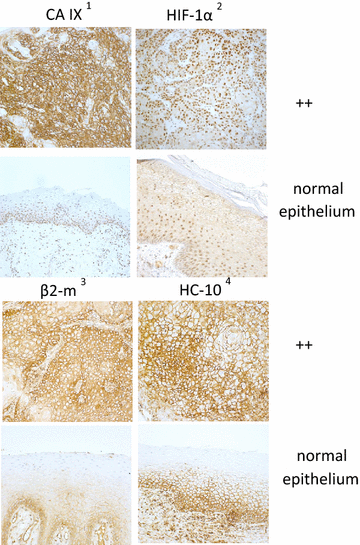
Results: Hypoxia is a frequent event in OSCC and leads to a reprogramming of the cellular metabolism in order to prevent cell death. Hypoxic OSCC cells induce different adaptive changes such as anaerobic glycolysis, pH stabilisation and alterations of the gene and protein expression profile. This complex metabolic program is orchestrated by the hypoxia inducible factor (HIF)-1, the master regulator of early tumor progression. Hypoxia-dependent and -independent alterations in immune surveillance lead to different immune evasion strategies, which are partially mediated by alterations of the tumor cells, changes in the frequency, activity and repertoire of immune cell infiltrates and of soluble and environmental factors of the tumor micromilieu with consecutive generation of an immune escape phenotype, progression of disease and poor clinical outcome of OSCC patients.
Conclusions: This review focusses on the importance of HIF-1 in the adaption and reprogramming of the metabolic system to reduced oxygen values as well as on the role of the tumor microenvironment for evasion of OSCC from immune recognition and destruction.
Keywords: Hypoxia; Immune escape; Immune response; Metabolic adaption; Oral squamous cell carcinoma.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Associations among pretreatment tumor necrosis and the expression of HIF-1α and PD-L1 in advanced oral squamous cell carcinoma and the prognostic impact thereof.Oral Oncol. 2015 Nov;51(11):1004-1010. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2015.08.011. Epub 2015 Sep 11. Oral Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26365985
-
Chemokines accentuating protumoral activities in oral cancer microenvironment possess an imperious stratagem for therapeutic resolutions.Oral Oncol. 2016 Sep;60:8-17. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2016.06.008. Epub 2016 Jun 29. Oral Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27531867 Review.
-
Regulation of PD-L1 expression in a high-grade invasive human oral squamous cell carcinoma microenvironment.Int J Oncol. 2017 Jan;50(1):41-48. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2016.3785. Epub 2016 Dec 2. Int J Oncol. 2017. PMID: 27922697 Free PMC article.
-
Transcutaneous carbon dioxide suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition in oral squamous cell carcinoma.Int J Oncol. 2016 Apr;48(4):1493-8. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2016.3380. Epub 2016 Feb 5. Int J Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26846904
-
Hypoxia induced EMT: A review on the mechanism of tumor progression and metastasis in OSCC.Oral Oncol. 2018 May;80:23-32. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2018.03.004. Epub 2018 Mar 21. Oral Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29706185 Review.
Cited by
-
The Oral Microbiota May Have Influence on Oral Cancer.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 Jan 15;9:476. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00476. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32010645 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of combination immunochemotherapies on progression of 4NQO-induced murine oral squamous cell carcinoma.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2019 Jul;68(7):1133-1141. doi: 10.1007/s00262-019-02348-2. Epub 2019 May 28. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2019. PMID: 31139925 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of an Immune Score-Based Gene Panel with Prognostic Power for Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Med Sci Monit. 2020 Jun 12;26:e922854. doi: 10.12659/MSM.922854. Med Sci Monit. 2020. PMID: 32529991 Free PMC article.
-
GP88/PGRN Serum Levels Are Associated with Prognosis for Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Patients.Biology (Basel). 2021 May 4;10(5):400. doi: 10.3390/biology10050400. Biology (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34064411 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic Cooperation and Competition in the Tumor Microenvironment: Implications for Therapy.Front Oncol. 2017 Apr 12;7:68. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2017.00068. eCollection 2017. Front Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28447025 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bussu F, Sali M, Gallus R, Vellone VG, Zannoni GF, Autorino R, Dinapoli N, Santangelo R, Martucci R, Graziani C, et al. HPV infection in squamous cell carcinomas arising from different mucosal sites of the head and neck region. Is p16 immunohistochemistry a reliable surrogate marker? Br J Cancer. 2013;108:1157–1162. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2013.55. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

