Inhibiting BACE1 to reverse synaptic dysfunctions in Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 27044452
- PMCID: PMC4856578
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2016.03.025
Inhibiting BACE1 to reverse synaptic dysfunctions in Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
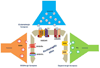
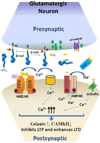
Over the past two decades, many studies have identified significant contributions of toxic β-amyloid peptides (Aβ) to the etiology of Alzheimer's disease (AD), which is the most common age-dependent neurodegenerative disease. AD is also recognized as a disease of synaptic failure. Aβ, generated by sequential proteolytic cleavages of amyloid precursor protein (APP) by BACE1 and γ-secretase, is one of major culprits that cause this failure. In this review, we summarize current findings on how BACE1-cleaved APP products impact learning and memory through proteins localized on glutamatergic, GABAergic, and dopaminergic synapses. Considering the broad effects of Aβ on all three types of synapses, BACE1 inhibition emerges as a practical approach for ameliorating Aβ-mediated synaptic dysfunctions. Since BACE1 inhibitory drugs are currently in clinical trials, this review also discusses potential complications arising from BACE1 inhibition. We emphasize that the benefits of BACE1 inhibitory drugs will outweigh the concerns.
Keywords: AMPA receptors; APP; Abeta peptides; Alzheimer’s β-secretase; BACE1; Dopamine receptors; NMDA receptors; Synapses.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation of Synaptic Amyloid-β Generation through BACE1 Retrograde Transport in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease.J Neurosci. 2017 Mar 8;37(10):2639-2655. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2851-16.2017. Epub 2017 Feb 3. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28159908 Free PMC article.
-
BACE1: the beta-secretase enzyme in Alzheimer's disease.J Mol Neurosci. 2004;23(1-2):105-14. doi: 10.1385/JMN:23:1-2:105. J Mol Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15126696 Review.
-
The beta-secretase, BACE: a prime drug target for Alzheimer's disease.J Mol Neurosci. 2001 Oct;17(2):157-70. doi: 10.1385/JMN:17:2:157. J Mol Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11816789 Review.
-
Amyloid-β protein (Aβ) Glu11 is the major β-secretase site of β-site amyloid-β precursor protein-cleaving enzyme 1(BACE1), and shifting the cleavage site to Aβ Asp1 contributes to Alzheimer pathogenesis.Eur J Neurosci. 2013 Jun;37(12):1962-9. doi: 10.1111/ejn.12235. Eur J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23773065
-
Protective effects of BACE1 inhibitory ligand molecules against amyloid beta-induced synaptic and mitochondrial toxicities in Alzheimer's disease.Hum Mol Genet. 2020 Jan 1;29(1):49-69. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddz227. Hum Mol Genet. 2020. PMID: 31595293 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Potential Effects of MSC-Derived Exosomes in Neuroplasticity in Alzheimer's Disease.Front Cell Neurosci. 2018 Sep 24;12:317. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2018.00317. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30319358 Free PMC article. Review.
-
3D culture models of Alzheimer's disease: a road map to a "cure-in-a-dish".Mol Neurodegener. 2016 Dec 9;11(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s13024-016-0139-7. Mol Neurodegener. 2016. PMID: 27938410 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Close Look at BACE1 Inhibitors for Alzheimer's Disease Treatment.CNS Drugs. 2019 Mar;33(3):251-263. doi: 10.1007/s40263-019-00613-7. CNS Drugs. 2019. PMID: 30830576 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BACE1 deletion in the adult mouse reverses preformed amyloid deposition and improves cognitive functions.J Exp Med. 2018 Mar 5;215(3):927-940. doi: 10.1084/jem.20171831. Epub 2018 Feb 14. J Exp Med. 2018. PMID: 29444819 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological Functions of the β-Site Amyloid Precursor Protein Cleaving Enzyme 1 and 2.Front Mol Neurosci. 2017 Apr 19;10:97. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2017.00097. eCollection 2017. Front Mol Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28469554 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abramov E, Dolev I, Fogel H, Ciccotosto GD, Ruff E, Slutsky I. Amyloid-beta as a positive endogenous regulator of release probability at hippocampal synapses. Nat Neurosci. 2009;12:1567–1576. - PubMed
-
- Allard P, Alafuzoff I, Carlsson A, Eriksson K, Ericson E, Gottfries CG, Marcusson JO. Loss of dopamine uptake sites labeled with [3H]GBR-12935 in Alzheimer’s disease. Eur Neurol. 1990;30:181–185. - PubMed
-
- Allinson TM, Parkin ET, Condon TP, Schwager SL, Sturrock ED, Turner AJ, Hooper NM. The role of ADAM10 and ADAM17 in the ectodomain shedding of angiotensin converting enzyme and the amyloid precursor protein. Eur J Biochem. 2004;271:2539–2547. - PubMed
-
- Almeida CG, Tampellini D, Takahashi RH, Greengard P, Lin MT, Snyder EM, Gouras GK. Beta-amyloid accumulation in APP mutant neurons reduces PSD-95 and GluR1 in synapses. Neurobiol Dis. 2005;20:187–198. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

