The systems biology format converter
- PMID: 27044654
- PMCID: PMC4820913
- DOI: 10.1186/s12859-016-1000-2
The systems biology format converter
Abstract
Background: Interoperability between formats is a recurring problem in systems biology research. Many tools have been developed to convert computational models from one format to another. However, they have been developed independently, resulting in redundancy of efforts and lack of synergy.
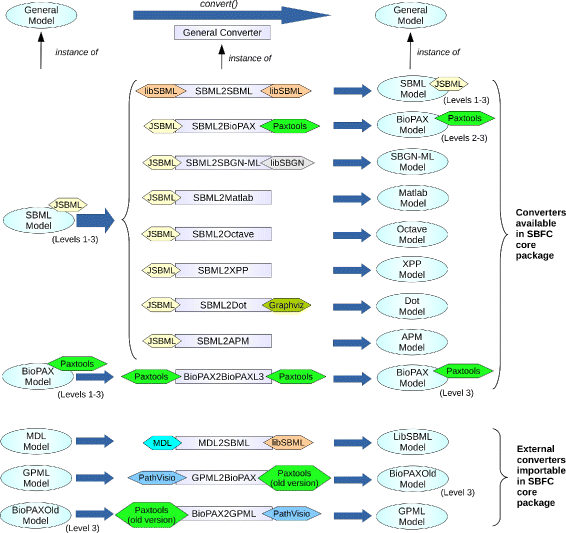
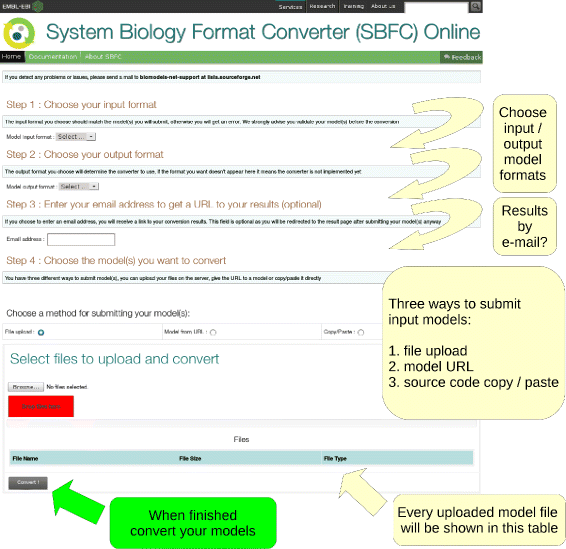
Results: Here we present the System Biology Format Converter (SBFC), which provide a generic framework to potentially convert any format into another. The framework currently includes several converters translating between the following formats: SBML, BioPAX, SBGN-ML, Matlab, Octave, XPP, GPML, Dot, MDL and APM. This software is written in Java and can be used as a standalone executable or web service.
Conclusions: The SBFC framework is an evolving software project. Existing converters can be used and improved, and new converters can be easily added, making SBFC useful to both modellers and developers. The source code and documentation of the framework are freely available from the project web site.
Keywords: Converter; Format; SBML; Systems biology.
Figures


References
-
- Juty N, Le Novére N, Laibe C. Identifiers.org and MIRIAM Registry: community resources to provide persistent identification. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40(D1):D580–D586. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1097. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

