MicroRNA-326 acts as a molecular switch in the regulation of midbrain urocortin 1 expression
- PMID: 27045550
- PMCID: PMC5008923
- DOI: 10.1503/jpn.150154
MicroRNA-326 acts as a molecular switch in the regulation of midbrain urocortin 1 expression
Abstract
Background: Altered levels of urocortin 1 (Ucn1) in the centrally projecting Edinger-Westphal nucleus (EWcp) of depressed suicide attempters or completers mediate the brain's response to stress, while the mechanism regulating Ucn1 expression is unknown. We tested the hypothesis that microRNAs (miRNAs), which are vital fine-tuners of gene expression during the brain's response to stress, have the capacity to modulate Ucn1 expression.
Methods: Computational analysis revealed that the Ucn1 3' untranslated region contained a conserved binding site for miR-326. We examined miR-326 and Ucn1 levels in the EWcp of depressed suicide completers. In addition, we evaluated miR-326 and Ucn1 levels in the serum and the EWcp of a chronic variable mild stress (CVMS) rat model of behavioural despair and after recovery from CVMS, respectively. Gain and loss of miR-326 function experiments examined the regulation of Ucn1 by this miRNA in cultured midbrain neurons.
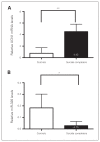
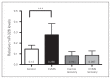
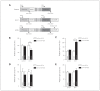
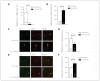
Results: We found reduced miR-326 levels concomitant with elevated Ucn1 levels in the EWcp of depressed suicide completers as well as in the EWcp of CVMS rats. In CVMS rats fully recovered from stress, both serum and EWcp miR-326 levels rebounded to nonstressed levels. While downregulation of miR-326 levels in primary midbrain neurons enhanced Ucn1 expression levels, miR-326 overexpression selectively reduced the levels of this neuropeptide.
Limitations: This study lacked experiments showing that in vivo alteration of miR-326 levels alleviate depression-like behaviours. We show only correlative data for miR-325 and cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript levels in the EWcp.
Conclusion: We identified miR-326 dysregulation in depressed suicide completers and characterized this miRNA as an upstream regulator of the Ucn1 neuropeptide expression in midbrain neurons.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
