FocusALL: Focal Stacking of Microscopic Images Using Modified Harris Corner Response Measure
- PMID: 27045831
- PMCID: PMC4888603
- DOI: 10.1109/TCBB.2015.2459685
FocusALL: Focal Stacking of Microscopic Images Using Modified Harris Corner Response Measure
Abstract
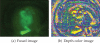
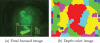
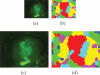
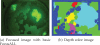
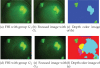
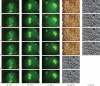
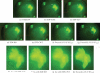
Automated image analysis of microscopic images such as protein crystallization images and cellular images is one of the important research areas. If objects in a scene appear at different depths with respect to the camera's focal point, objects outside the depth of field usually appear blurred. Therefore, scientists capture a collection of images with different depths of field. Focal stacking is a technique of creating a single focused image from a stack of images collected with different depths of field. In this paper, we introduce a novel focal stacking technique, FocusALL, which is based on our modified Harris Corner Response Measure. We also propose enhanced FocusALL for application on images collected under high resolution and varying illumination. FocusALL resolves problems related to the assumption that focus regions have high contrast and high intensity. Especially, FocusALL generates sharper boundaries around protein crystal regions and good in focus images for high resolution images in reasonable time. FocusALL outperforms other methods on protein crystallization images and performs comparably well on other datasets such as retinal epithelial images and simulated datasets.
Figures










References
-
- Harris C, Stephens M. Alvey vision conference. Vol. 15. Manchester, UK: 1988. A combined corner and edge detector. p. 50.
-
- Stauffer NL. Active auto focus system improvement. 1983 Jan 4; US Patent 4,367,027.
-
- Bezzubik VV, Ustinov SN, Belashenkov NR. Optimization of algorithms for autofocusing a digital microscope. Journal of Optical Technology. 2009;76(10):603–608.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

