Detection of genes mediating beta-lactamase production in isolates of enterobacteria recovered from wild pets in Saudi Arabia
- PMID: 27047051
- PMCID: PMC4774817
- DOI: 10.14202/vetworld.2015.1400-1404
Detection of genes mediating beta-lactamase production in isolates of enterobacteria recovered from wild pets in Saudi Arabia
Abstract
Aim: To determine the genetic basis and types of beta-lactamase encountered among enterobacterial isolates of wild pets from the animal exhibit.
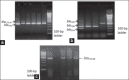
Materials and methods: A total of 17 beta-lactamase-producing enterobacteria recovered from fecal samples of wild pet animals were analyzed for a selected beta-lactamase gene by polymerase chain reaction.
Results: Molecular analysis identified one or more β-lactamase-encoding genes in 14 enterobacterial isolates as a single or gene combination. The most frequent extended-spectrum β-lactamases types were TEM and CTX-M, and the most common AmpC enzymes were CMY-2 and DHA types.
Conclusions: The study is the first in Saudi Arabia, have established the presence of β-lactamase-encoding genes in the fecal isolates of wild pets.
Keywords: Saudi Arabia; animal exhibit; extended-spectrum β-lactamases/AmpC beta-lactamase; fecal samples; polymerase chain reaction.
Figures
References
-
- Dolejska M, Cizek A, Literak I. High prevalence of antimicrobial-resistant genes and integrons in Escherichia coli isolates from black-headed gulls in the Czech Republic. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007;103:11–19. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
