The use of poly(styrene-block-isobutylene-block-styrene) as a microshunt to treat glaucoma
- PMID: 27047682
- PMCID: PMC4817329
- DOI: 10.1093/rb/rbw005
The use of poly(styrene-block-isobutylene-block-styrene) as a microshunt to treat glaucoma
Abstract
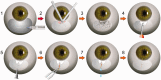
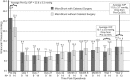
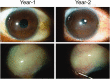
The InnFocus MicroShunt® is a minimally invasive glaucoma drainage microtube used to shunt aqueous humor from the anterior chamber of the eye to a flap formed under the conjunctiva and Tenon's capsule. The safety and clinical performance of this device approaches that of trabeculectomy with mitomycin C, the current 'gold standard' treatment for advanced glaucoma. The invention of a new biomaterial called poly(styrene-block-isobutylene-block-styrene) or 'SIBS' is the enabling factor which led to the success of this product. SIBS is ultrastable with virtually no foreign body reaction in the body, which manifests as clinically insignificant inflammation and capsule formation in the eye. The lack of capsule formation enables unobstructed flow through the 70 µm lumen tube and the achievement of controlled low intraocular pressure, which is important for the management of glaucoma. This article summarizes the integration of SIBS into a glaucoma drainage device and confirms its functionality with clinical success over a 2-year period.
Keywords: biocompatibility; medical device; soft tissue; stent.
Figures


References
-
- Pinchuk L. A review of the biostability and carcinogenicity of polyurethanes in medicine and the new generation of ‘biostable’ polyurethanes. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed 1994;6:225–67. - PubMed
-
- Kennedy JP, Ivan B. Designed Polymers by Carbocationic Macromolecular Engineering: Theory and Practice. New York: Oxford University Press, 1991.
-
- Pinchuk L. Biostable Elastomeric Polymers Having Quaternary Carbons. US Patent 5,741,331, 21 April 1998.
-
- Pinchuk L. Method of Implanting Biostable Elastomeric Polymers Having Quaternary Carbons. US Patent 6,102,939, 15 August 2000.
-
- Pinchuk L, Wilson GJ, Barry JJ. et al. Medical applications of poly(styrene-block-isobutylene-block-styrene) (“SIBS”). Biomaterials 2008;29:448–60. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

