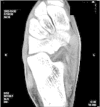
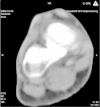
CUBOID-NAVICULAR TARSAL COALITION
- PMID: 27047815
- PMCID: PMC4799214
- DOI: 10.1016/S2255-4971(15)30443-2
CUBOID-NAVICULAR TARSAL COALITION
Abstract
The authors present the case of a nine-year-old female patient who presented with pain in her right foot associated with physical activities. After this case was diagnosed as cuboid-navicular tarsal coalition, the patient was treated surgically with resection of the coalition, thereby resolving the symptoms. The literature was reviewed and the importance of adequate physical examination and imaging assessment for investigating foot pain in children and adolescents was discussed.
Keywords: Foot Deformities, congenital/surgery; Subtalar Joint; Tarsal Bones/surgery.
Figures
References
-
- Stormont DM, Peterson HA. The relative incidence of tarsal coalition. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1983;(181):181–186. - PubMed
-
- Holl M. Beitrage zur chirurgischen osteologie dês fusses. Arch Klin Chir. 1880;25:211.
-
- Tachdjian MO. The foot and leg. Tarsal coalition. In: Tachdjian MO, editor. Pediatric orthopedics. 2a. ed. Saunders; Philadelphia: 1990. pp. 2578–2611.
-
- Johnson TR, Mizel MS, Temple T. Cuboid-navicular tarsal coalition – presentation and treatment: a case report and review of the literature. Foot Ankle Int. 2005;26(3):264–266. - PubMed
-
- Waugh W. Partial cubo-navicular coalition as a cause of peroneal spastic flat foot. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1957;39(3):520–523. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources