BIOMECHANICAL ACCESS METHOD FOR ANALYZING ISOMETRICITY IN RECONSTRUCTING THE MEDIAL PATELLOFEMORAL LIGAMENT
- PMID: 27047872
- PMCID: PMC4799453
- DOI: 10.1016/S2255-4971(15)30010-0
BIOMECHANICAL ACCESS METHOD FOR ANALYZING ISOMETRICITY IN RECONSTRUCTING THE MEDIAL PATELLOFEMORAL LIGAMENT
Abstract
Objective: To present a biomechanical device for evaluating medial patellofemoral ligament (MPFL) reconstruction and its isometricity.
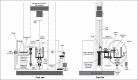
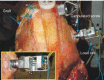
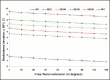
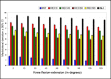
Methods: An accessible biomechanical method that allowed application of physiological and non-physiological forces to the knee using a mechanical arm and application of weights and counterweights was developed, so as to enable many different evaluations and have a very accurate measurement system for distances between different structures, for analysis on experiments. This article describes the assembly of this system, and suggests some practical applications. Six cadaver knees were studied. The knees were prepared in a testing machine developed at the Biomechanics Laboratory of IOT-HCFMUSP, which allowed dynamic evaluation of patellar behavior, with quantification of patellar lateralization between 0° and 120°. The differences between the distances found with and without load applied to the patella were grouped according to the graft fixation angle (0°, 30°, 60° or 90°) and knee position (intact, damaged or reconstructed).
Results: There was a tendency for smaller lateral displacement to occur at fixation angles greater than 30 degrees of flexion, especially between the angles of 45° and 60° degrees of flexion, after the reconstruction. For the other angles, there was no statistical significance.
Conclusion: The method developed is a useful tool for studies on the patellofemoral joint and the MPFL, and has a very accurate measurement system for distances between different structures. It can be used in institutions with fewer resources available.
Keywords: Biomechanics; Joint Instability; Knee/surgery; Patellar Ligament.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The effect of femoral tunnel position and graft tension on patellar contact mechanics and kinematics after medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction.Am J Sports Med. 2014 Feb;42(2):364-72. doi: 10.1177/0363546513509230. Epub 2013 Nov 25. Am J Sports Med. 2014. PMID: 24275861
-
The ability of medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction to correct patellar kinematics and contact mechanics in the presence of a lateralized tibial tubercle.Am J Sports Med. 2015 Sep;43(9):2198-207. doi: 10.1177/0363546515597906. Epub 2015 Aug 19. Am J Sports Med. 2015. PMID: 26290576
-
Effect of Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction Method on Patellofemoral Contact Pressures and Kinematics.Am J Sports Med. 2016 May;44(5):1186-94. doi: 10.1177/0363546516631736. Epub 2016 Mar 4. Am J Sports Med. 2016. PMID: 26944575
-
Properties and Function of the Medial Patellofemoral Ligament: A Systematic Review.Am J Sports Med. 2020 Mar;48(3):754-766. doi: 10.1177/0363546519841304. Epub 2019 May 15. Am J Sports Med. 2020. PMID: 31091114
-
Knee Flexion Angle During Graft Fixation for Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction: A Systematic Review of Outcomes and Complications.Arthroscopy. 2019 Jun;35(6):1893-1904. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2018.11.071. Epub 2019 Apr 4. Arthroscopy. 2019. PMID: 30954322
Cited by
-
Reconstruction of the medial patellofemoral ligament by means of the anatomical double-bundle technique using metal anchors.Rev Bras Ortop. 2016 Apr 27;51(3):290-7. doi: 10.1016/j.rboe.2015.07.011. eCollection 2016 May-Jun. Rev Bras Ortop. 2016. PMID: 27274482 Free PMC article.
-
Biomechanical comparison of single- and double-bundle medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction.J Orthop Surg Res. 2017 Feb 13;12(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s13018-017-0530-2. J Orthop Surg Res. 2017. PMID: 28193295 Free PMC article.
-
Medial patellofemoral ligament and medial patellotibial ligament reconstruction in children: preliminary results.Rev Bras Ortop. 2017 Jul 5;52(4):417-422. doi: 10.1016/j.rboe.2017.06.011. eCollection 2017 Jun-Jul. Rev Bras Ortop. 2017. PMID: 28884099 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Conlan T, Garth WP, Jr, Lemons JE. Evaluation of the medial soft-tissue restraints of the extensor mechanism of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1993;75(5):682–693. - PubMed
-
- Desio SM, Burks RT, Bachus KN. Soft tissue restraints to lateral patellar translation in the human knee. Am J Sports Med. 1998;26(1):59–65. - PubMed
-
- Steensen RN, Dopirak RM, Maurus PB. A simple technique for reconstruction of the medial patellofemoral ligament using a quadriceps tendon graft. Arthroscopy. 2005;21(3):365–370. - PubMed
-
- Sallay PI, Poggi J, Speer KP, Garrett WE. Acute dislocation of the patella. A correlative pathoanatomic study. Am J Sports Med. 1996;24(1):52–60. - PubMed
-
- Sanders TG, Morrison WB, Singleton BA, Miller MD, Cornum KG. Medial patellofemoral ligament injury following acute transient dislocation of the patella: MR findings with surgical correlation in 14 patients. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2001;25(6):957–962. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
