EPIDEMIOLOGICAL STUDY ON TENDON RUPTURES OF THE KNEE EXTENSOR MECHANISM AT A LEVEL 1 HOSPITAL
- PMID: 27047890
- PMCID: PMC4799490
- DOI: 10.1016/S2255-4971(15)30028-8
EPIDEMIOLOGICAL STUDY ON TENDON RUPTURES OF THE KNEE EXTENSOR MECHANISM AT A LEVEL 1 HOSPITAL
Abstract
Objectives: The purpose of the present study was to review the epidemiological aspects of tendon ruptures of the knee extensor apparatus at a level 1 hospital.
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed 76 lesions of the knee extensor apparatus that were treated surgically at the Miguel Couto Municipal Hospital between March 2004 and March 2011. We took into consideration age, sex, trauma mechanism, anatomical classification of the lesion, affected side, comorbidities and associated lesions.
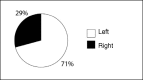
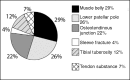
Results: Among the patients studied, 68 were male and the mean age was 36 years. Regarding the trauma mechanism, 62 lesions occurred due to direct trauma; the right side was affected in 21 cases; eight presented comorbidities and four presented associated lesions.
Conclusion: The majority of the patients were male, at an economically active age (young people), and were victims of direct trauma. Ruptures of the patellar ligament were the most frequent lesions. Associated lesions were rare and comorbidities were infrequent in our sample.
Keywords: Epidemiology; Knee; Rupture.
Figures
References
-
- Newberg A, Wales L. Radiographic diagnosis of quadriceps tendon rupture. Radiology. 1977;125(2):367–371. - PubMed
-
- Kellersmann R, Blattert TR, Weckbach A. Bilateral patellar tendon rupture without predisposing systemic disease or steroid use: a case report and review of the literature. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2005;125(2):127–133. - PubMed
-
- Clayton RA, Court-Brown CM. The epidemiology of musculoskeletal tendinous and ligamentous injuries. Injury. 2008;39(12):1338–1344. - PubMed
-
- Zernicke RF, Garhammer J, Jobe FW. Human patellar tendon rupture. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1977;59(2):179–183. - PubMed
-
- Enad JG. Patellar tendon ruptures. South Med J. 1999;92(6):563–566. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources