B-cell-specific conditional expression of Myd88p.L252P leads to the development of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in mice
- PMID: 27048211
- PMCID: PMC4891954
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2015-11-684183
B-cell-specific conditional expression of Myd88p.L252P leads to the development of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in mice
Abstract
The adaptor protein MYD88 is critical for relaying activation of Toll-like receptor signaling to NF-κB activation. MYD88 mutations, particularly the p.L265P mutation, have been described in numerous distinct B-cell malignancies, including diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). Twenty-nine percent of activated B-cell-type DLBCL (ABC-DLBCL), which is characterized by constitutive activation of the NF-κB pathway, carry the p.L265P mutation. In addition, ABC-DLBCL frequently displays focal copy number gains affecting BCL2 Here, we generated a novel mouse model in which Cre-mediated recombination, specifically in B cells, leads to the conditional expression of Myd88(p.L252P) (the orthologous position of the human MYD88(p.L265P) mutation) from the endogenous locus. These mice develop a lymphoproliferative disease and occasional transformation into clonal lymphomas. The clonal disease displays the morphologic and immunophenotypical characteristics of ABC-DLBCL. Lymphomagenesis can be accelerated by crossing in a further novel allele, which mediates conditional overexpression of BCL2 Cross-validation experiments in human DLBCL samples revealed that both MYD88 and CD79B mutations are substantially enriched in ABC-DLBCL compared with germinal center B-cell DLBCL. Furthermore, analyses of human DLBCL genome sequencing data confirmed that BCL2 amplifications frequently co-occurred with MYD88 mutations, further validating our approach. Finally, in silico experiments revealed that MYD88-mutant ABC-DLBCL cells in particular display an actionable addiction to BCL2. Altogether, we generated a novel autochthonous mouse model of ABC-DLBCL that could be used as a preclinical platform for the development and validation of novel therapeutic approaches for the treatment of ABC-DLBCL.
Figures
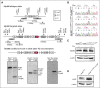
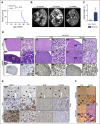
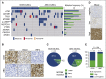
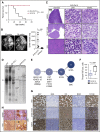
Comment in
-
Mouse model of MYD88L265P-dependent DLBCL.Blood. 2016 Jun 2;127(22):2660-1. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-04-710434. Blood. 2016. PMID: 27257177 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Oncogenically active MYD88 mutations in human lymphoma.Nature. 2011 Feb 3;470(7332):115-9. doi: 10.1038/nature09671. Epub 2010 Dec 22. Nature. 2011. PMID: 21179087 Free PMC article.
-
Rewired NFκB signaling as a potentially actionable feature of activated B-cell-like diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.Eur J Haematol. 2016 Dec;97(6):499-510. doi: 10.1111/ejh.12792. Epub 2016 Sep 8. Eur J Haematol. 2016. PMID: 27526684 Review.
-
Frequent MYD88 L265P and CD79B Mutations in Primary Breast Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma.Am J Surg Pathol. 2016 Mar;40(3):324-34. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000000592. Am J Surg Pathol. 2016. PMID: 26752547
-
An Autochthonous Mouse Model of Myd88- and BCL2-Driven Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma Reveals Actionable Molecular Vulnerabilities.Blood Cancer Discov. 2021 Jan;2(1):70-91. doi: 10.1158/2643-3230.BCD-19-0059. Blood Cancer Discov. 2021. PMID: 33447829 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Pathogenesis of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma.J Clin Exp Hematop. 2016;56(2):71-78. doi: 10.3960/jslrt.56.71. J Clin Exp Hematop. 2016. PMID: 27980305 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An Aged/Autoimmune B-cell Program Defines the Early Transformation of Extranodal Lymphomas.Cancer Discov. 2023 Jan 9;13(1):216-243. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-22-0561. Cancer Discov. 2023. PMID: 36264161 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Treatment Strategies in the Management of Waldenström Macroglobulinemia.Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2020 Feb;15(1):31-43. doi: 10.1007/s11899-020-00559-4. Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2020. PMID: 32006301 Review.
-
Mouse Models in the Study of Mature B-Cell Malignancies.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2021 Apr 1;11(4):a034827. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a034827. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2021. PMID: 32398289 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-affinity T-cell receptor specific for MyD88 L265P mutation for adoptive T-cell therapy of B-cell malignancies.J Immunother Cancer. 2021 Jul;9(7):e002410. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2021-002410. J Immunother Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34330762 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic cooperation and crosstalk between MYD88L265P and mutations that dysregulate CD79B and surface IgM.J Exp Med. 2017 Sep 4;214(9):2759-2776. doi: 10.1084/jem.20161454. Epub 2017 Jul 12. J Exp Med. 2017. PMID: 28701369 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

