Lipopolysaccharide Preconditioning Induces an Anti-inflammatory Phenotype in BV2 Microglia
- PMID: 27048218
- PMCID: PMC11482333
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-015-0324-1
Lipopolysaccharide Preconditioning Induces an Anti-inflammatory Phenotype in BV2 Microglia
Abstract
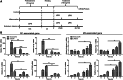
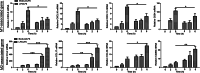
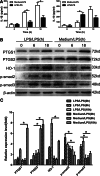
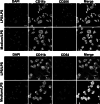
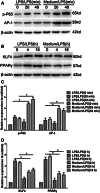
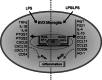
Increasing evidence indicates that endotoxin tolerance is an essential immune-homeostatic response to repeated exposure to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) that induces a state of altered responsiveness in macrophage, resulting in repression of pro-inflammatory gene expression and increased expression of factors that mediate the resolution of inflammation. In this study, quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction and Western blot for M1 and M2 markers were performed to characterize phenotypic changes of BV2 microglia. We found that the cytokine and chemokine expression during endotoxin tolerance were mostly similar to those found during M2 polarization. We further examined the expression of M1 and M2 markers in CD11b+ BV2 by double immunofluorescent staining. The expression of M2 markers (CD206) increased, whereas the expression of M1 (CD54) markers reduced during endotoxin tolerance. Moreover, expression of different transcription factor, known for their function in the regulation of pro- and anti-inflammatory reaction, was also different. Our data demonstrate that repeat LPS treatment activates a differentiation program that leads to microglial polarization toward M2-like phenotype.
Keywords: Alternative activation; Anti-inflammatory; Endotoxin tolerance; Mice; Microglia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Curcumin inhibits LPS-induced neuroinflammation by promoting microglial M2 polarization via TREM2/ TLR4/ NF-κB pathways in BV2 cells.Mol Immunol. 2019 Dec;116:29-37. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2019.09.020. Epub 2019 Oct 4. Mol Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31590042
-
The effects of insulin on the inflammatory activity of BV2 microglia.PLoS One. 2018 Aug 27;13(8):e0201878. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0201878. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30148836 Free PMC article.
-
Lipopolysaccharide preconditioning facilitates M2 activation of resident microglia after spinal cord injury.J Neurosci Res. 2014 Dec;92(12):1647-58. doi: 10.1002/jnr.23448. Epub 2014 Jul 10. J Neurosci Res. 2014. PMID: 25044014
-
The flavonoid rutin modulates microglial/macrophage activation to a CD150/CD206 M2 phenotype.Chem Biol Interact. 2017 Aug 25;274:89-99. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2017.07.004. Epub 2017 Jul 8. Chem Biol Interact. 2017. PMID: 28693884
-
Polarization profiles of human M-CSF-generated macrophages and comparison of M1-markers in classically activated macrophages from GM-CSF and M-CSF origin.Cell Immunol. 2013 Jan;281(1):51-61. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2013.01.010. Epub 2013 Feb 4. Cell Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23454681
Cited by
-
LPS-Activated Microglial Cell-Derived Conditioned Medium Protects HT22 Neuronal Cells against Glutamate-Induced Ferroptosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 2;24(3):2910. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032910. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36769233 Free PMC article.
-
A unique hybrid characteristic having both pro- and anti-inflammatory phenotype transformed by repetitive low-dose lipopolysaccharide in C8-B4 microglia.Sci Rep. 2020 Jun 2;10(1):8945. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-65998-8. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32488176 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia inducible factor-1α regulates microglial innate immune memory and the pathology of Parkinson's disease.J Neuroinflammation. 2024 Mar 30;21(1):80. doi: 10.1186/s12974-024-03070-2. J Neuroinflammation. 2024. PMID: 38555419 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Microglia and Macrophage Polarization via Apoptosis Signal-Regulating Kinase 1 Silencing after Ischemic/Hypoxic Injury.Front Mol Neurosci. 2017 Aug 14;10:261. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2017.00261. eCollection 2017. Front Mol Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28855861 Free PMC article.
-
Folic Acid Is Able to Polarize the Inflammatory Response in LPS Activated Microglia by Regulating Multiple Signaling Pathways.Mediators Inflamm. 2016;2016:5240127. doi: 10.1155/2016/5240127. Epub 2016 Sep 25. Mediators Inflamm. 2016. PMID: 27738387 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akira S, Uematsu S, Takeuchi O (2006) Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell 124(4):783–801 - PubMed
-
- Biswas SK, Lopez-Collazo E (2009) Endotoxin tolerance: new mechanisms, molecules and clinical significance. Trends Immunol 30(10):475–487 - PubMed
-
- Boche D, Cunningham C, Gauldie J, Perry VH (2003) Transforming growth factor-beta 1-mediated neuroprotection against excitotoxic injury in vivo. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 23(10):1174–1182 - PubMed
-
- Buttini M, Limonta S, Boddeke HW (1996) Peripheral administration of lipopolysaccharide induces activation of microglial cells in rat brain. Neurochem Int 29(1):25–35 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

