p53 in the DNA-Damage-Repair Process
- PMID: 27048304
- PMCID: PMC4852800
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a026070
p53 in the DNA-Damage-Repair Process
Abstract
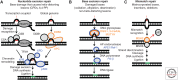
The cells in the human body are continuously challenged by a variety of genotoxic attacks. Erroneous repair of the DNA can lead to mutations and chromosomal aberrations that can alter the functions of tumor suppressor genes or oncogenes, thus causing cancer development. As a central tumor suppressor, p53 guards the genome by orchestrating a variety of DNA-damage-response (DDR) mechanisms. Already early in metazoan evolution, p53 started controlling the apoptotic demise of genomically compromised cells. p53 plays a prominent role as a facilitator of DNA repair by halting the cell cycle to allow time for the repair machineries to restore genome stability. In addition, p53 took on diverse roles to also directly impact the activity of various DNA-repair systems. It thus appears as if p53 is multitasking in providing protection from cancer development by maintaining genome stability.
Copyright © 2016 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; all rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
p53 mRNA Metabolism Links with the DNA Damage Response.Genes (Basel). 2021 Sep 20;12(9):1446. doi: 10.3390/genes12091446. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34573428 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[DNA damage-induced signal pathway of p53 as a tumor suppressor and the gene mutation in human cancer].Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 2000 Jul;45(10):1742-51. Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 2000. PMID: 10897687 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
-
Unraveling the Guardian: p53's Multifaceted Role in the DNA Damage Response and Tumor Treatment Strategies.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 1;25(23):12928. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312928. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684639 Free PMC article. Review.
-
p53 modulation of the DNA damage response.J Cell Biochem. 2007 Mar 1;100(4):883-96. doi: 10.1002/jcb.21091. J Cell Biochem. 2007. PMID: 17031865 Review.
-
p53 and regulation of DNA damage recognition during nucleotide excision repair.DNA Repair (Amst). 2003 Sep 18;2(9):947-54. doi: 10.1016/s1568-7864(03)00087-9. DNA Repair (Amst). 2003. PMID: 12967652 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical significance of p53 protein expression and TP53 variation status in colorectal cancer.BMC Cancer. 2022 Aug 31;22(1):940. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-10039-y. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 36045334 Free PMC article.
-
DNA-Dependent Protein Kinase Inhibitor Peposertib Potentiates the Cytotoxicity of Topoisomerase II Inhibitors in Synovial Sarcoma Models.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Dec 30;16(1):189. doi: 10.3390/cancers16010189. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38201616 Free PMC article.
-
Natural Chalcones and Derivatives in Colon Cancer: Pre-Clinical Challenges and the Promise of Chalcone-Based Nanoparticles.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Dec 1;15(12):2718. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15122718. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 38140059 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Obesity-Induced Macrophages during Preneoplastic Growth Promotes Mammary Epithelial Stem/Progenitor Activity, DNA Damage, and Tumor Formation.Cancer Res. 2020 Oct 15;80(20):4465-4475. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-0789. Epub 2020 Aug 31. Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32868380 Free PMC article.
-
Amelioration of Radiation-Induced Cell Death in Neuro2a Cells by Neutralizing Oxidative Stress and Reducing Mitochondrial Dysfunction Using N-Acetyl-L-Tryptophan.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Nov 26;2022:9124365. doi: 10.1155/2022/9124365. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 36471866 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Achanta G, Huang P. 2004. Role of p53 in sensing oxidative DNA damage in response to reactive oxygen species-generating agents. Cancer Res 64: 6233–6239. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
