Transplantation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells expressing elastin alleviates pelvic floor dysfunction
- PMID: 27048404
- PMCID: PMC4822266
- DOI: 10.1186/s13287-016-0308-1
Transplantation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells expressing elastin alleviates pelvic floor dysfunction
Abstract
Background: Pelvic floor dysfunction (PFD) is a group of clinical conditions including stress urinary incontinence (SUI) and pelvic organ prolapse (POP). The abnormality of collagen and elastin metabolism in pelvic connective tissues is implicated in SUI and POP.
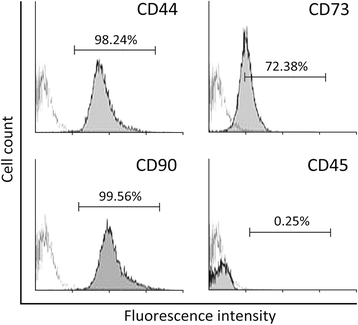
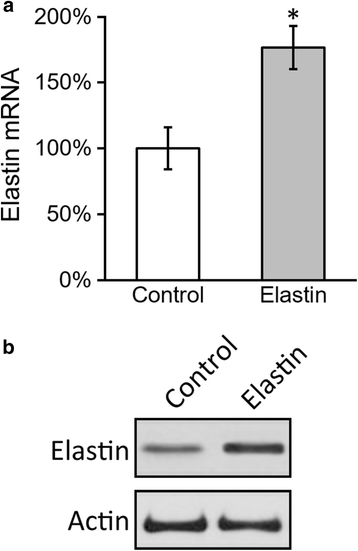
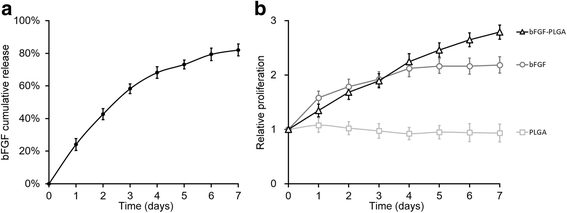
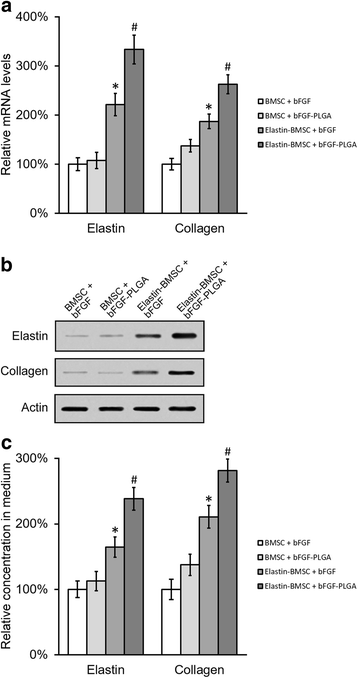
Methods: To reconstitute the connective tissues with normal distribution of collagen and elastin, we transduced elastin to bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BMSC). Elastin-expressing BMSCs were then differentiated to fibroblasts using bFGF, which produced collagen and elastin. To achieve the sustained release of bFGF, we formulated bFGF in poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) nanoparticles (NP).
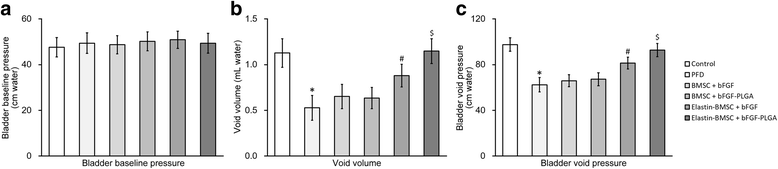
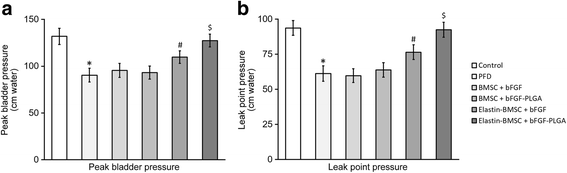
Results: In an in vitro cell culture system of 7 days, when no additional bFGF was administrated, the initial PLGA-loaded bFGF NP induced prolonged production of collagen and elastin from elastin-expressing BMSCs. In vivo, co-injection of PLGA-loaded bFGF NP and elastin-expressing BMSCs into the PFD rats significantly improved the outcome of urodynamic tests. Together, these results provided an efficient model of connective tissue engineering using BMSC and injectable PLGA-loaded growth factors.
Conclusions: Our results provided the first instance of a multidisciplinary approach, combining both stem cell and nanoparticle technologies, for the treatment of PFD.
Keywords: Basic fibroblast growth factor; Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells; Pelvic floor dysfunction; Stress urinary incontinence.
Figures
References
-
- Alvarez J, Cvach K, Dwyer P. Complications in pelvic floor surgery. Minerva Ginecol. 2013;65:53–67. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

