Secreted frizzled related protein 1 protects H9C2 cells from hypoxia/re-oxygenation injury by blocking the Wnt signaling pathway
- PMID: 27048460
- PMCID: PMC4822324
- DOI: 10.1186/s12944-016-0240-5
Secreted frizzled related protein 1 protects H9C2 cells from hypoxia/re-oxygenation injury by blocking the Wnt signaling pathway
Abstract
Background: In animal models, secreted frizzled related protein 1 (Sfrp1) inhibition of the Wnt signaling pathway is beneficial because Sfrp1 reduces myocardial apoptosis and prevents heart failure. The mechanisms mediating the cellular survival effect of Sfrp1 has not been completely elucidated. The present study was designed to investigate the possible protective actions of Sfrp1 on cardiac muscle cells using an in vitro model of ischemia/reperfusion, and to evaluate the possible involvement of the Wnt signaling pathway.
Methods: We used a recombinant AAV9 vector to deliver the Sfrp1 gene into H9C2 rat cardiomyoblasts and adopted an in vitro model of ischemia/reperfusion. Cell vitality was measured by CKK-8 and the trypan blue exclusion assay. Western blot was used to evaluate the expression of Dvl-1, β-catenin, c-Myc, Bax, and Bcl-2. Flow cytometry analysis of cardiomyocyte apoptosis was performed.
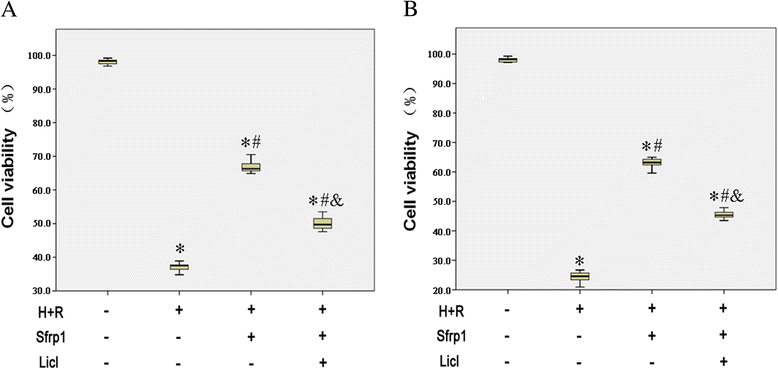
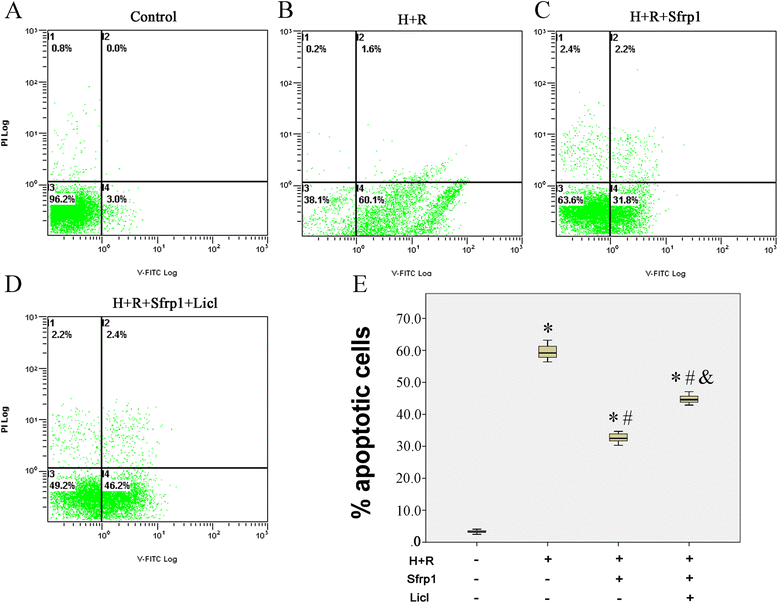
Results: We confirmed that Sfrp1 significantly increased cell viability (assayed by trypan blue and CKK-8) and decreased apoptosis (assayed by flow cytometry analysis and the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio). These effects were partly attributable to the ability of Sfrp1 to down-regulate Wnt signaling pathway (assayed by Western blot to evaluate the expression of Dvl-1, β-catenin, and c-Myc). Indeed, reactivation of the Wnt signaling pathway activity with the specific activator, Licl, reduced Sfrp1-induced cardioprotection during hypoxia and reoxygenation.
Conclusions: The present study demonstrated that Sfrp1 directly protected H9C2 cells from hypoxia and reoxygenation-induced reperfusion injury and apoptosis through inhibition of the Wnt signaling pathway, and added new mechanistic insight regarding the cardioprotective role of Sfrp1 on ischemic damage.
Keywords: Apoptosis; H9C2; Hypoxia reoxygenation injury; Sfrp1; Wnt signaling pathway.
Figures



Similar articles
-
FrzA gene protects cardiomyocytes from H2O2-induced oxidative stress through restraining the Wnt/Frizzled pathway.Lipids Health Dis. 2015 Aug 18;14:90. doi: 10.1186/s12944-015-0088-0. Lipids Health Dis. 2015. PMID: 26282432 Free PMC article.
-
Sfrp1 attenuates TAC-induced cardiac dysfunction by inhibiting Wnt signaling pathway- mediated myocardial apoptosis in mice.Lipids Health Dis. 2018 Aug 28;17(1):202. doi: 10.1186/s12944-018-0832-3. Lipids Health Dis. 2018. PMID: 30153824 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of miR-148b ameliorates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via regulation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Aug;234(10):17757-17766. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28401. Epub 2019 Feb 28. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30820984
-
Wnt/β-catenin in ischemic myocardium: interactions and signaling pathways as a therapeutic target.Heart Fail Rev. 2019 May;24(3):411-419. doi: 10.1007/s10741-018-9759-z. Heart Fail Rev. 2019. PMID: 30539334 Review.
-
The advantages and disadvantages of sfrp1 and sfrp2 expression in pathological events.Tohoku J Exp Med. 2010 May;221(1):11-7. doi: 10.1620/tjem.221.11. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2010. PMID: 20448436 Review.
Cited by
-
Potential Effects of Corneal Cross-Linking upon the Limbus.Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:5062064. doi: 10.1155/2016/5062064. Epub 2016 Sep 5. Biomed Res Int. 2016. PMID: 27689081 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wnt Signaling Inhibitors as Therapeutic Approach in Ischemic Heart Disease.Molecules. 2024 Dec 17;29(24):5958. doi: 10.3390/molecules29245958. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39770047 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recombinant dsAAV9-mediated Endogenous Overexpression of Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor Alleviates Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury via Activating AMPK and ERK1/2 Signaling Pathways.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2025 Jan 2. doi: 10.1007/s10557-024-07662-1. Online ahead of print. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2025. PMID: 39747743
-
Secreted Frizzled Related Proteins in Cardiovascular and Metabolic Diseases.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Aug 20;12:712217. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.712217. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34489867 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Large Clostridial Toxins: Mechanisms and Roles in Disease.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2021 Aug 18;85(3):e0006421. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00064-21. Epub 2021 Jun 2. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2021. PMID: 34076506 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

