Plasma Metabolomic Changes following PI3K Inhibition as Pharmacodynamic Biomarkers: Preclinical Discovery to Phase I Trial Evaluation
- PMID: 27048952
- PMCID: PMC5321508
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-15-0815
Plasma Metabolomic Changes following PI3K Inhibition as Pharmacodynamic Biomarkers: Preclinical Discovery to Phase I Trial Evaluation
Abstract
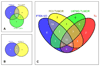
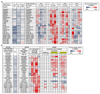
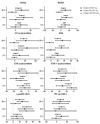
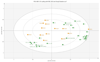
PI3K plays a key role in cellular metabolism and cancer. Using a mass spectrometry-based metabolomics platform, we discovered that plasma concentrations of 26 metabolites, including amino acids, acylcarnitines, and phosphatidylcholines, were decreased in mice bearing PTEN-deficient tumors compared with non-tumor-bearing controls and in addition were increased following dosing with class I PI3K inhibitor pictilisib (GDC-0941). These candidate metabolomics biomarkers were evaluated in a phase I dose-escalation clinical trial of pictilisib. Time- and dose-dependent effects were observed in patients for 22 plasma metabolites. The changes exceeded baseline variability, resolved after drug washout, and were recapitulated on continuous dosing. Our study provides a link between modulation of the PI3K pathway and changes in the plasma metabolome and demonstrates that plasma metabolomics is a feasible and promising strategy for biomarker evaluation. Also, our findings provide additional support for an association between insulin resistance, branched-chain amino acids, and related metabolites following PI3K inhibition. Mol Cancer Ther; 15(6); 1412-24. ©2016 AACR.
©2016 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Yap TA, Sandhu SK, Workman P, de Bono JS. Envisioning the future of early anticancer drug development. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010;10:514–23. - PubMed
-
- Sarker D, Workman P. Pharmacodynamic biomarkers for molecular cancer therapeutics. Adv Cancer Res. 2007;96:213–68. - PubMed
-
- Workman P. How much gets there and what does it do?: The need for better pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic endpoints in contemporary drug discovery and development. Curr Pharm Des. 2003;9:891–902. - PubMed
-
- Yap TA, Lorente D, Omlin A, Olmos D, de Bono JS. Circulating tumor cells: a multifunctional biomarker. Clin Cancer Res. 2014;20:2553–68. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

