Wnt9A Induction Linked to Suppression of Human Colorectal Cancer Cell Proliferation
- PMID: 27049382
- PMCID: PMC4848951
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms17040495
Wnt9A Induction Linked to Suppression of Human Colorectal Cancer Cell Proliferation
Abstract
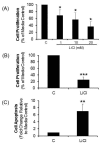
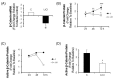
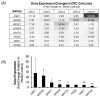
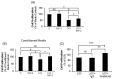
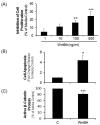
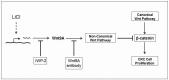
Most studies of Wnt signaling in malignant tissues have focused on the canonical Wnt pathway (CWP) due to its role in stimulating cellular proliferation. The role of the non-canonical Wnt pathway (NCWP) in tissues with dysregulated Wnt signaling is not fully understood. Understanding NCWP's role is important since these opposing pathways act in concert to maintain homeostasis in healthy tissues. Our preliminary studies demonstrated that LiCl inhibited proliferation of primary cells derived from colorectal cancer (CRC). Since LiCl stimulates cell proliferation in normal tissues and NCWP suppresses it, the present study was designed to investigate the impact of NCWP components in LiCl-mediated effects. LiCl-mediated inhibition of CRC cell proliferation (p < 0.001) and increased apoptosis (p < 0.01) coincided with 23-fold increase (p < 0.025) in the expression of the NCWP ligand, Wnt9A. LiCl also suppressed β-catenin mRNA (p < 0.03), total β-catenin protein (p < 0.025) and the active form of β-catenin. LiCl-mediated inhibition of CRC cell proliferation was partially reversed by IWP-2, and Wnt9A antibody. Recombinant Wnt9A protein emulated LiCl effects by suppressing β-catenin protein (p < 0.001), inhibiting proliferation (p < 0.001) and increasing apoptosis (p < 0.03). This is the first study to demonstrate induction of a NCWP ligand, Wnt9A as part of a mechanism for LiCl-mediated suppression of CRC cell proliferation.
Keywords: LiCl; Wnt pathway ligand; Wnt9A; canonical Wnt pathway; human colorectal cancer; non-canonical Wnt pathway; β-catenin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Raddeanin A inhibits growth and induces apoptosis in human colorectal cancer through downregulating the Wnt/β-catenin and NF-κB signaling pathway.Life Sci. 2018 Aug 15;207:532-549. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2018.06.035. Epub 2018 Jul 1. Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 29972765
-
Activation of the canonical WNT signaling pathway promotes ovarian surface epithelial proliferation without inducing β-catenin/Tcf-mediated reporter expression.Dev Dyn. 2013 Mar;242(3):291-300. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.23919. Epub 2013 Feb 6. Dev Dyn. 2013. PMID: 23239518
-
A novel ent-kaurane diterpenoid executes antitumor function in colorectal cancer cells by inhibiting Wnt/β-catenin signaling.Carcinogenesis. 2015 Mar;36(3):318-26. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgv003. Epub 2015 Jan 18. Carcinogenesis. 2015. PMID: 25600769
-
Therapeutic potential of targeting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in colorectal cancer.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Feb;110:473-481. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.11.082. Epub 2018 Dec 6. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 30530050 Review.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Targeting Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway in Treatment of Colorectal Cancer: Rational and Progress.J Cell Biochem. 2017 Aug;118(8):1979-1983. doi: 10.1002/jcb.25903. Epub 2017 Apr 25. J Cell Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28109136 Review.
Cited by
-
Emerging Roles of Wnt Ligands in Human Colorectal Cancer.Front Oncol. 2020 Aug 14;10:1341. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01341. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32923386 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of Wnt7b reduces the proliferation, invasion, and migration of colorectal cancer cells.Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Feb;50(2):1415-1424. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-08106-5. Epub 2022 Dec 6. Mol Biol Rep. 2023. PMID: 36472725
-
Modeling cartilage pathology in mucopolysaccharidosis VI using iPSCs reveals early dysregulation of chondrogenic and metabolic gene expression.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Dec 6;10:949063. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.949063. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 36561048 Free PMC article.
-
ERα and ERβ Homodimers in the Same Cellular Context Regulate Distinct Transcriptomes and Functions.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Jul 6;13:930227. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.930227. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35872983 Free PMC article.
-
WNT9A and WNT9B in Development and Disease.Differentiation. 2025 Mar-Apr;142:100820. doi: 10.1016/j.diff.2024.100820. Epub 2024 Nov 22. Differentiation. 2025. PMID: 39616032 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

