Structural basis for ligand-dependent dimerization of phenylalanine hydroxylase regulatory domain
- PMID: 27049649
- PMCID: PMC4822156
- DOI: 10.1038/srep23748
Structural basis for ligand-dependent dimerization of phenylalanine hydroxylase regulatory domain
Abstract
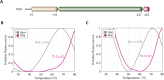
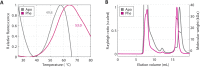
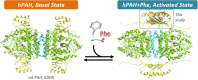
The multi-domain enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) catalyzes the hydroxylation of dietary I-phenylalanine (Phe) to I-tyrosine. Inherited mutations that result in PAH enzyme deficiency are the genetic cause of the autosomal recessive disorder phenylketonuria. Phe is the substrate for the PAH active site, but also an allosteric ligand that increases enzyme activity. Phe has been proposed to bind, in addition to the catalytic domain, a site at the PAH N-terminal regulatory domain (PAH-RD), to activate the enzyme via an unclear mechanism. Here we report the crystal structure of human PAH-RD bound with Phe at 1.8 Å resolution, revealing a homodimer of ACT folds with Phe bound at the dimer interface. This work delivers the structural evidence to support previous solution studies that a binding site exists in the RD for Phe, and that Phe binding results in dimerization of PAH-RD. Consistent with our structural observation, a disease-associated PAH mutant impaired in Phe binding disrupts the monomer:dimer equilibrium of PAH-RD. Our data therefore support an emerging model of PAH allosteric regulation, whereby Phe binds to PAH-RD and mediates the dimerization of regulatory modules that would bring about conformational changes to activate the enzyme.
Figures


References
-
- Konecki D. S. & Lichter-Konecki U. The phenylketonuria locus: current knowledge about alleles and mutations of the phenylalanine hydroxylase gene in various populations. Hum. Genet. 87, 377–388 (1991). - PubMed
-
- Kobe B. et al. Structural basis of autoregulation of phenylalanine hydroxylase. Nat. Struct. Biol. 6, 442–448 (1999). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

