Brigatinib, an anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibitor, abrogates activity and growth in ALK-positive neuroblastoma cells, Drosophila and mice
- PMID: 27049722
- PMCID: PMC5045374
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.8508
Brigatinib, an anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibitor, abrogates activity and growth in ALK-positive neuroblastoma cells, Drosophila and mice
Abstract
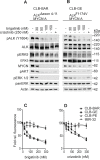
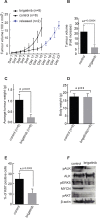
Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) is a tyrosine kinase receptor which has been implicated in numerous solid and hematologic cancers. ALK mutations are reported in about 5-7% of neuroblastoma cases but the ALK-positive percentage increases significantly in the relapsed patient population. Crizotinib, the first clinically approved ALK inhibitor for the treatment of ALK-positive lung cancer has had less dramatic responses in neuroblastoma. Here we investigate the efficacy of a second-generation ALK inhibitor, brigatinib, in a neuroblastoma setting. Employing neuroblastoma cell lines, mouse xenograft and Drosophila melanogaster model systems expressing different constitutively active ALK variants, we show clear and efficient inhibition of ALK activity by brigatinib. Similar abrogation of ALK activity was observed in vitro employing a set of different constitutively active ALK variants in biochemical assays. These results suggest that brigatinib is an effective inhibitor of ALK kinase activity in ALK addicted neuroblastoma that should be considered as a potential future therapeutic option for ALK-positive neuroblastoma patients alone or in combination with other treatments.
Keywords: AP26113; anaplastic lymphoma kinase; brigatinib; neuroblastoma; resistant mutations.
Conflict of interest statement
V.M.R. is full-time employee of ARIAD Pharmaceuticals and holds ARIAD stock. There are no other relationships, conditions or circumstances that present a potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The Potent ALK Inhibitor Brigatinib (AP26113) Overcomes Mechanisms of Resistance to First- and Second-Generation ALK Inhibitors in Preclinical Models.Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Nov 15;22(22):5527-5538. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-0569. Epub 2016 Oct 25. Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27780853
-
Discovery of Brigatinib (AP26113), a Phosphine Oxide-Containing, Potent, Orally Active Inhibitor of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase.J Med Chem. 2016 May 26;59(10):4948-64. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b00306. Epub 2016 May 12. J Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 27144831
-
CEP-28122, a highly potent and selective orally active inhibitor of anaplastic lymphoma kinase with antitumor activity in experimental models of human cancers.Mol Cancer Ther. 2012 Mar;11(3):670-9. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-11-0776. Epub 2011 Dec 27. Mol Cancer Ther. 2012. PMID: 22203728
-
Brigatinib for the treatment of ALK-positive advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients.Drugs Today (Barc). 2017 Aug;53(8):435-446. doi: 10.1358/dot.2017.53.8.2676119. Drugs Today (Barc). 2017. PMID: 29119148 Review.
-
Brigatinib for ALK-positive metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: design, development and place in therapy.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019 Feb 8;13:569-580. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S147499. eCollection 2019. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019. PMID: 30804663 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ALK in Neuroblastoma: Biological and Therapeutic Implications.Cancers (Basel). 2018 Apr 10;10(4):113. doi: 10.3390/cancers10040113. Cancers (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29642598 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel multiple tyrosine kinase inhibitor ponatinib inhibits bFGF-activated signaling in neuroblastoma cells and suppresses neuroblastoma growth in vivo.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 24;8(4):5874-5884. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11580. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 27564113 Free PMC article.
-
The targetable kinase PIM1 drives ALK inhibitor resistance in high-risk neuroblastoma independent of MYCN status.Nat Commun. 2019 Nov 28;10(1):5428. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13315-x. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31780656 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting anaplastic lymphoma kinase in neuroblastoma.APMIS. 2019 May;127(5):288-302. doi: 10.1111/apm.12940. Epub 2019 Apr 3. APMIS. 2019. PMID: 30803032 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small Molecule Inhibitors as Therapeutic Agents Targeting Oncogenic Fusion Proteins: Current Status and Clinical.Molecules. 2023 Jun 9;28(12):4672. doi: 10.3390/molecules28124672. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37375228 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Morris SW, Kirstein MN, Valentine MB, Dittmer KG, Shapiro DN, Saltman DL, Look AT. Fusion of a kinase gene, ALK, to a nucleolar protein gene, NPM, in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Science. 1994;263:1281–1284. - PubMed
-
- Marino-Enriquez A, Dal Cin P. ALK as a paradigm of oncogenic promiscuity: different mechanisms of activation and different fusion partners drive tumors of different lineages. Cancer Genet. 2013;206:357–373. - PubMed
-
- Hallberg B, Palmer RH. Mechanistic insight into ALK receptor tyrosine kinase in human cancer biology. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013;13:685–700. - PubMed
-
- (FDA). U.F.a.D.A FDA approves Xalkori with companion diagnostic for a type of late-stage lung cancer. 2011 http://wwwfdagov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/ucm269856htm
-
- (Roche) Japan becomes first country to approve Roche's alectinib for people with a specific form of advanced lung cancer. 2014 http://wwwrochecom/media/store/releases/med-cor-2014-07-04htm
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

