Modulation of tissue repair by regeneration enhancer elements
- PMID: 27049946
- PMCID: PMC4844022
- DOI: 10.1038/nature17644
Modulation of tissue repair by regeneration enhancer elements
Abstract
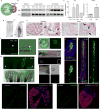
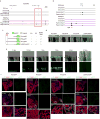
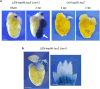
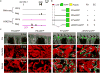
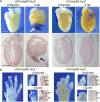
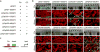
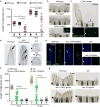
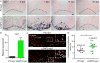
How tissue regeneration programs are triggered by injury has received limited research attention. Here we investigate the existence of enhancer regulatory elements that are activated in regenerating tissue. Transcriptomic analyses reveal that leptin b (lepb) is highly induced in regenerating hearts and fins of zebrafish. Epigenetic profiling identified a short DNA sequence element upstream and distal to lepb that acquires open chromatin marks during regeneration and enables injury-dependent expression from minimal promoters. This element could activate expression in injured neonatal mouse tissues and was divisible into tissue-specific modules sufficient for expression in regenerating zebrafish fins or hearts. Simple enhancer-effector transgenes employing lepb-linked sequences upstream of pro- or anti-regenerative factors controlled the efficacy of regeneration in zebrafish. Our findings provide evidence for 'tissue regeneration enhancer elements' (TREEs) that trigger gene expression in injury sites and can be engineered to modulate the regenerative potential of vertebrate organs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests. Readers are welcome to comment on the online version of the paper.
Figures








References
-
- Nacu E, Tanaka EM. Limb regeneration: a new development? Ann Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2011;27:409–440. - PubMed
-
- Whitehead GG, Makino S, Lien CL, Keating M. T fgf20 is essential for initiating zebrafish fin regeneration. Science. 2005;310:1957–1960. - PubMed
-
- Wehner D, Weidinger G. Signaling networks organizing regenerative growth of the zebrafish fin. Trends Genet. 2015;31:336–343. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

