Medulloblastoma Genotype Dictates Blood Brain Barrier Phenotype
- PMID: 27050100
- PMCID: PMC4829447
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2016.03.002
Medulloblastoma Genotype Dictates Blood Brain Barrier Phenotype
Abstract
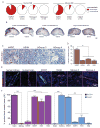
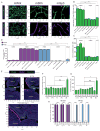
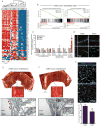
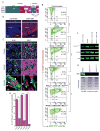
The childhood brain tumor, medulloblastoma, includes four subtypes with very different prognoses. Here, we show that paracrine signals driven by mutant β-catenin in WNT-medulloblastoma, an essentially curable form of the disease, induce an aberrant fenestrated vasculature that permits the accumulation of high levels of intra-tumoral chemotherapy and a robust therapeutic response. In contrast, SHH-medulloblastoma, a less curable disease subtype, contains an intact blood brain barrier, rendering this tumor impermeable and resistant to chemotherapy. The medulloblastoma-endothelial cell paracrine axis can be manipulated in vivo, altering chemotherapy permeability and clinical response. Thus, medulloblastoma genotype dictates tumor vessel phenotype, explaining in part the disparate prognoses among medulloblastoma subtypes and suggesting an approach to enhance the chemoresponsiveness of other brain tumors.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


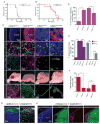
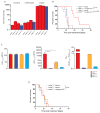
Comment in
-
Blood-Brain Barrier Breakdown Determines Differential Therapeutic Outcome in Genetically Diverse Forms of Medulloblastoma.Cancer Cell. 2016 Apr 11;29(4):427-429. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2016.03.024. Cancer Cell. 2016. PMID: 27070693
-
CNS cancer: Wnt affects blood-brain barrier permeabilty.Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2016 Jun;13(6):330. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2016.63. Epub 2016 Apr 19. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27092953 No abstract available.
References
-
- Alvarez JI, Dodelet-Devillers A, Kebir H, Ifergan I, Fabre PJ, Terouz S, Sabbagh M, Wosik K, Bourbonniere L, Bernard M, et al. The Hedgehog pathway promotes blood-brain barrier integrity and CNS immune quiescence. Science. 2011;334:1727–1731. - PubMed
-
- Armulik A, Genove G, Mae M, Nisancioglu MH, Wallgard E, Niaudet C, He L, Norlin J, Lindblom P, Strittmatter K, et al. Pericytes regulate the blood-brain barrier. Nature. 2010;468:557–561. - PubMed
-
- Avula S, Mallucci C, Kumar R, Pizer B. Posterior fossa syndrome following brain tumour resection: review of pathophysiology and a new hypothesis on its pathogenesis. Child's nervous system : ChNS : official journal of the International Society for Pediatric Neurosurgery. 2015;31:1859–1867. - PubMed
-
- Biechele TL, Adams AM, Moon RT. Transcription-based reporters of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2009;2009 pdb prot5223. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

