Metabolomics-assisted proteomics identifies succinylation and SIRT5 as important regulators of cardiac function
- PMID: 27051063
- PMCID: PMC4843474
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1519858113
Metabolomics-assisted proteomics identifies succinylation and SIRT5 as important regulators of cardiac function
Abstract
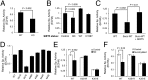
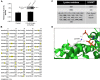
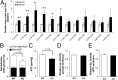
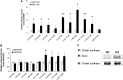
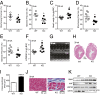
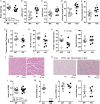
Cellular metabolites, such as acyl-CoA, can modify proteins, leading to protein posttranslational modifications (PTMs). One such PTM is lysine succinylation, which is regulated by sirtuin 5 (SIRT5). Although numerous proteins are modified by lysine succinylation, the physiological significance of lysine succinylation and SIRT5 remains elusive. Here, by profiling acyl-CoA molecules in various mouse tissues, we have discovered that different tissues have different acyl-CoA profiles and that succinyl-CoA is the most abundant acyl-CoA molecule in the heart. This interesting observation has prompted us to examine protein lysine succinylation in different mouse tissues in the presence and absence of SIRT5. Protein lysine succinylation predominantly accumulates in the heart whenSirt5is deleted. Using proteomic studies, we have identified many cardiac proteins regulated by SIRT5. Our data suggest that ECHA, a protein involved in fatty acid oxidation, is a major enzyme that is regulated by SIRT5 and affects heart function.Sirt5knockout (KO) mice have lower ECHA activity, increased long-chain acyl-CoAs, and decreased ATP in the heart under fasting conditions.Sirt5KO mice develop hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, as evident from the increased heart weight relative to body weight, as well as reduced shortening and ejection fractions. These findings establish that regulating heart metabolism and function is a major physiological function of lysine succinylation and SIRT5.
Keywords: desuccinylation; fatty acid metabolism; hypertrophic cardiomyopathy; lysine succinylation; sirtuin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

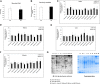
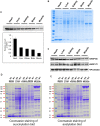
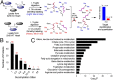
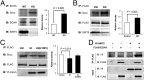

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA193256/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD016191/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG043930/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR025449/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R00 CA168997/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA163255/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM098596/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008500/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020541/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32GM008500/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 CA201963/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 1S10RR025449-01/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

