Production of α1,3-galactosyltransferase targeted pigs using transcription activator-like effector nuclease-mediated genome editing technology
- PMID: 27051344
- PMCID: PMC4808648
- DOI: 10.4142/jvs.2016.17.1.89
Production of α1,3-galactosyltransferase targeted pigs using transcription activator-like effector nuclease-mediated genome editing technology
Abstract
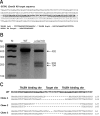
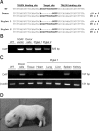
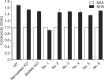
Recent developments in genome editing technology using meganucleases demonstrate an efficient method of producing gene edited pigs. In this study, we examined the effectiveness of the transcription activator-like effector nuclease (TALEN) system in generating specific mutations on the pig genome. Specific TALEN was designed to induce a double-strand break on exon 9 of the porcine α1,3-galactosyltransferase (GGTA1) gene as it is the main cause of hyperacute rejection after xenotransplantation. Human decay-accelerating factor (hDAF) gene, which can produce a complement inhibitor to protect cells from complement attack after xenotransplantation, was also integrated into the genome simultaneously. Plasmids coding for the TALEN pair and hDAF gene were transfected into porcine cells by electroporation to disrupt the porcine GGTA1 gene and express hDAF. The transfected cells were then sorted using a biotin-labeled IB4 lectin attached to magnetic beads to obtain GGTA1 deficient cells. As a result, we established GGTA1 knockout (KO) cell lines with biallelic modification (35.0%) and GGTA1 KO cell lines expressing hDAF (13.0%). When these cells were used for somatic cell nuclear transfer, we successfully obtained live GGTA1 KO pigs expressing hDAF. Our results demonstrate that TALEN-mediated genome editing is efficient and can be successfully used to generate gene edited pigs.
Keywords: alpha-1,3-galactosyltransferase; cloned pig; human decay-accelerating factor; knockout; somatic cell nuclear transfer.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficient generation of GGTA1-null Diannan miniature pigs using TALENs combined with somatic cell nuclear transfer.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2016 Nov 8;14(1):77. doi: 10.1186/s12958-016-0212-7. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2016. PMID: 27821126 Free PMC article.
-
Inclusion of homologous DNA in nuclease-mediated gene targeting facilitates a higher incidence of bi-allelically modified cells.Xenotransplantation. 2015 Sep-Oct;22(5):379-90. doi: 10.1111/xen.12194. Xenotransplantation. 2015. PMID: 26381494 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient production of biallelic GGTA1 knockout pigs by cytoplasmic microinjection of CRISPR/Cas9 into zygotes.Xenotransplantation. 2016 Sep;23(5):338-46. doi: 10.1111/xen.12258. Epub 2016 Sep 9. Xenotransplantation. 2016. PMID: 27610605
-
Progress in producing knockout models for xenotransplantation by nuclear transfer.Ann Med. 2002;34(7-8):501-6. doi: 10.1080/078538902321117706. Ann Med. 2002. PMID: 12553489 Review.
-
Xenotransplantation of solid organs in the pig-to-primate model.Transpl Immunol. 2009 Jun;21(2):87-92. doi: 10.1016/j.trim.2008.10.005. Epub 2008 Oct 26. Transpl Immunol. 2009. PMID: 18955143 Review.
Cited by
-
Current status of the application of gene editing in pigs.J Reprod Dev. 2021 Jun 21;67(3):177-187. doi: 10.1262/jrd.2021-025. Epub 2021 Apr 10. J Reprod Dev. 2021. PMID: 33840678 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of Genetically Engineered Pigs in Biomedical Research.Genes (Basel). 2020 Jun 19;11(6):670. doi: 10.3390/genes11060670. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32575461 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficient Generation of Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer-Competent Porcine Cells with Mutated Alleles at Multiple Target Loci by Using CRISPR/Cas9 Combined with Targeted Toxin-Based Selection System.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Dec 4;18(12):2610. doi: 10.3390/ijms18122610. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29207527 Free PMC article.
-
Production of genetically modified pigs expressing human insulin and C-peptide as a source of islets for xenotransplantation.Transgenic Res. 2019 Dec;28(5-6):549-559. doi: 10.1007/s11248-019-00169-8. Epub 2019 Aug 31. Transgenic Res. 2019. PMID: 31473874
-
Insight into the molecular mechanism of miR-192 regulating Escherichia coli resistance in piglets.Biosci Rep. 2018 Feb 21;38(1):BSR20171160. doi: 10.1042/BSR20171160. Print 2018 Feb 28. Biosci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29363554 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aigner B, Klymiuk N, Wolf E. Transgenic pigs for xenotransplantation: selection of promoter sequences for reliable transgene expression. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2010;15:201–206. - PubMed
-
- Baldan N, Rigotti P, Calabrese F, Cadrobbi R, Dedja A, Iacopetti I, Boldrin M, Seveso M, Dall'Olmo L, Frison L, De Benedictis G, Bernardini D, Thiene G, Cozzi E, Ancona E. Ureteral stenosis in HDAF pig-to-primate renal xenotransplantation: a phenomenon related to immunological events? Am J Transplant. 2004;4:475–481. - PubMed
-
- Boch J, Bonas U. Xanthomonas AvrBs3 family-type III effectors: discovery and function. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2010;48:419–436. - PubMed
-
- Chen G, Sun H, Yang H, Kubelik D, Garcia B, Luo Y, Xiang Y, Qian A, Copeman L, Liu W, Cardella CJ, Wang W, Xiong Y, Wall W, White DJ, Zhong R. The role of anti-non-Gal antibodies in the development of acute humoral xenograft rejection of hDAF transgenic porcine kidneys in baboons receiving anti-Gal antibody neutralization therapy. Transplantation. 2006;81:273–283. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

