Human Metabolic Enzymes Deficiency: A Genetic Mutation Based Approach
- PMID: 27051561
- PMCID: PMC4804091
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/9828672
Human Metabolic Enzymes Deficiency: A Genetic Mutation Based Approach
Abstract
One of the extreme challenges in biology is to ameliorate the understanding of the mechanisms which emphasize metabolic enzyme deficiency (MED) and how these pretend to have influence on human health. However, it has been manifested that MED could be either inherited as inborn error of metabolism (IEM) or acquired, which carries a high risk of interrupted biochemical reactions. Enzyme deficiency results in accumulation of toxic compounds that may disrupt normal organ functions and cause failure in producing crucial biological compounds and other intermediates. The MED related disorders cover widespread clinical presentations and can involve almost any organ system. To sum up the causal factors of almost all the MED-associated disorders, we decided to embark on a less traveled but nonetheless relevant direction, by focusing our attention on associated gene family products, regulation of their expression, genetic mutation, and mutation types. In addition, the review also outlines the clinical presentations as well as diagnostic and therapeutic approaches.
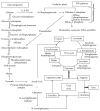
Figures
References
-
- Sharma S., Kumar P., Agarwal R., Kabra M., Deorari A., Paul V. Approach to inborn errors of metabolism presenting in the neonate. Indian Journal of Pediatrics. 2010;75(3):271–276. - PubMed
-
- Barshop B. A. Metabolic disease. Genetics. 2003;3:37–46.
-
- National Institutes of Health. NINDS, handout on lipid storage diseases fact sheet. NIH Publication. 2005;(05-2628)
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources