The role of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in predicting acute kidney injury in patients undergoing off-pump coronary artery bypass graft: A pilot study
- PMID: 27052061
- PMCID: PMC4900357
- DOI: 10.4103/0971-9784.179590
The role of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in predicting acute kidney injury in patients undergoing off-pump coronary artery bypass graft: A pilot study
Abstract
Objective: Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a commonly encountered postoperative complication after cardiac surgery especially in high risk patients. AKI though seen more commonly after conventional on pump coronary artery bypass surgery (CCABG), is not uncommon after off pump coronary bypass surgery (OPCAB). Various biomarkers have shown promise over last one decade as an early marker for predicting AKI postoperatively. NGAL is one such biomarker whose concentration is increased in urine after any nephrotoxic and ischemic insult. The objective of this study was to assess the role of urine NGAL in predicting AKI after OPCAB in patients with increased risk of developing AKI.
Design: A prospective cohort study.
Setting: A clinical study in a multi specialty hospital.
Participants: Eighty patients.
Materials and methods: study was approved by the hospital research ethics committee. 80 patients posted for OPCAB with an increased risk of developing AKI defined as having a Cleveland Clinic Foundation Acute renal failure scoring System score of ≥6 were included in the study. Patients with coronary angiography (CAG) within 48 hrs prior to surgery, pre-existing AKI, preoperative renal replacement therapy (RRT) and CKD stage 5 were excluded. Urine NGAL level before the start of surgery baseline and at 4 hrs post surgery were done. Renal function tests were assessed on the day of surgery (4 hrs post surgery) and on the next three days.
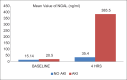
Result: Seven patients developed AKI as defined by acute kidney infection network (AKIN) and risk injury failure loss end stage (RIFLE) criteria for AKI. NGAL value at 4 hrs in patients who developed AKI was significantly higher than in those patients who did not develop AKI (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: urine NGAL is an early biomarker of acute kidney injury in patients undergoing OPCAB surgeries. However, large multicentre studies may be needed to confirm it.
Figures
References
-
- Conlon PJ, Stafford-Smith M, White WD, Newman MF, King S, Winn MP, et al. Acute renal failure following cardiac surgery. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1999;14:1158–62. - PubMed
-
- Mangano CM, Diamondstone LS, Ramsay JG, Aggarwal A, Herskowitz A, Mangano DT. Renal dysfunction after myocardial revascularization: Risk factors, adverse outcomes, and hospital resource utilization. The Multicenter Study of Perioperative Ischemia Research Group. Ann Intern Med. 1998;128:194–203. - PubMed
-
- Rosner MH, Okusa MD. Acute kidney injury associated with cardiac surgery. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;1:19–32. - PubMed
-
- Lassnigg A, Schmidlin D, Mouhieddine M, Bachmann LM, Druml W, Bauer P, et al. Minimal changes of serum creatinine predict prognosis in patients after cardiothoracic surgery: A prospective cohort study. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004;15:1597–605. - PubMed
-
- Thakar CV, Worley S, Arrigain S, Yared JP, Paganini EP. Influence of renal dysfunction on mortality after cardiac surgery: Modifying effect of preoperative renal function. Kidney Int. 2005;67:1112–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous