Atlas of prostate cancer heritability in European and African-American men pinpoints tissue-specific regulation
- PMID: 27052111
- PMCID: PMC4829663
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms10979
Atlas of prostate cancer heritability in European and African-American men pinpoints tissue-specific regulation
Abstract
Although genome-wide association studies have identified over 100 risk loci that explain ∼33% of familial risk for prostate cancer (PrCa), their functional effects on risk remain largely unknown. Here we use genotype data from 59,089 men of European and African American ancestries combined with cell-type-specific epigenetic data to build a genomic atlas of single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) heritability in PrCa. We find significant differences in heritability between variants in prostate-relevant epigenetic marks defined in normal versus tumour tissue as well as between tissue and cell lines. The majority of SNP heritability lies in regions marked by H3k27 acetylation in prostate adenoc7arcinoma cell line (LNCaP) or by DNaseI hypersensitive sites in cancer cell lines. We find a high degree of similarity between European and African American ancestries suggesting a similar genetic architecture from common variation underlying PrCa risk. Our findings showcase the power of integrating functional annotation with genetic data to understand the genetic basis of PrCa.
Figures

 is labelled by the dashed lines. Error bars show analytical standard error of estimate.
is labelled by the dashed lines. Error bars show analytical standard error of estimate.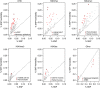
 equal to %SNPs after accounting for all tests. The two most significant annotations in each class are shown with triangle/cross, respectively, and labelled in bottom right (see Supplementary Data for all annotations).
equal to %SNPs after accounting for all tests. The two most significant annotations in each class are shown with triangle/cross, respectively, and labelled in bottom right (see Supplementary Data for all annotations).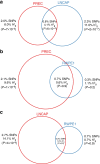
 and %SNP, with bold representing significance after correcting for nine tests. The observed trend is LNCAP>PREC>RWPE1: (a)
and %SNP, with bold representing significance after correcting for nine tests. The observed trend is LNCAP>PREC>RWPE1: (a) in LNCaP DHS was nominally significantly higher than PrEC (P=0.01); and
in LNCaP DHS was nominally significantly higher than PrEC (P=0.01); and  in LNCaP and PrEC was significantly higher than RWPE1 (b,c; P=1.5 × 10−9, P=1.2 × 10−5, respectively). All P values computed by Z-test using
in LNCaP and PrEC was significantly higher than RWPE1 (b,c; P=1.5 × 10−9, P=1.2 × 10−5, respectively). All P values computed by Z-test using  estimate and analytical standard error.
estimate and analytical standard error.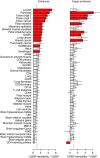
 / %SNP for enhancers (left) and super enhancers (right) from a given cell type tested marginally. Red indicates significant difference from 1.0 (no enrichment) after accounting for 49 tests. Enhancer LNCAP is most significant, with other cancers also appearing significant and non-cancer tissues least significant. Error bars show analytical s.e. of estimate.
/ %SNP for enhancers (left) and super enhancers (right) from a given cell type tested marginally. Red indicates significant difference from 1.0 (no enrichment) after accounting for 49 tests. Enhancer LNCAP is most significant, with other cancers also appearing significant and non-cancer tissues least significant. Error bars show analytical s.e. of estimate.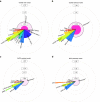
 under the null of no enrichment. Volume of each shaded pie-chart slice represents the actual
under the null of no enrichment. Volume of each shaded pie-chart slice represents the actual  inferred by the model. Slices extending outside/inside the middle pie correspond to enrichment/depletion in SNP heritability, as indicated by the dotted lines. Colour coding is consistent across all subpanels. * (**) denotes significant deviation at P<0.05 (P<0.05/15) of fraction of SNP heritability (
inferred by the model. Slices extending outside/inside the middle pie correspond to enrichment/depletion in SNP heritability, as indicated by the dotted lines. Colour coding is consistent across all subpanels. * (**) denotes significant deviation at P<0.05 (P<0.05/15) of fraction of SNP heritability ( from null model of
from null model of  by Z-test; see Supplementary Table 6 for P values).
by Z-test; see Supplementary Table 6 for P values).References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
- CA54281/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 17528/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- R01CA082664/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- G0401527/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 CA063464/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA098758/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA092579/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA042014/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 16491/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- G0500966/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- CA128978/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 CA197449/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016672/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- C522/A8649/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- F32 GM106584/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA037429/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 1 U19 CA148537-01/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- C5047/A7357/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- C1287/A10710/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- MR/N003284/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 CA194393/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- C16913/A6135/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- P30 CA68485/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189974/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA092447/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA188392/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- C12292/A11174/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- R01CA056678/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- C8197/A10123/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- U19 AI111224/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30CA042014/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 1U19 CA148065/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- C5047/A10692/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 076113/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01CA72818/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM107427/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 102215/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- C5047/A3354/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 1U19 CA148537/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA056678/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA63464/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- C490/A10124/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- C5047/A8384/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- R01 CA193910/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA128978/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA060553/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_PC_15018/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 CA072818/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 14136/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- U19 CA148537/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- C5047/A15007/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 15007/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- R01 CA082664/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA054281/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA063464/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA068485/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- G0500966/75466/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 75466/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 AR063759/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA128813/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 19170/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 1U19 CA148112/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM105857/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U19 CA148112/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 CA148065/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 10119/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- C8197/A10865/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- R01CA128813/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- C1281/A12014/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- R01 MH101244/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES011126/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- CA098758/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA092579/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 001/WHO_/World Health Organization/International
- R01 CA188392/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA164973/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA054281/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- C1287/A10118/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- UM1 CA182883/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 10124/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- G9815508/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 13065/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

