Cyclodextrin promotes atherosclerosis regression via macrophage reprogramming
- PMID: 27053774
- PMCID: PMC4878149
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aad6100
Cyclodextrin promotes atherosclerosis regression via macrophage reprogramming
Abstract
Atherosclerosis is an inflammatory disease linked to elevated blood cholesterol concentrations. Despite ongoing advances in the prevention and treatment of atherosclerosis, cardiovascular disease remains the leading cause of death worldwide. Continuous retention of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins in the subendothelial space causes a local overabundance of free cholesterol. Because cholesterol accumulation and deposition of cholesterol crystals (CCs) trigger a complex inflammatory response, we tested the efficacy of the cyclic oligosaccharide 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (CD), a compound that increases cholesterol solubility in preventing and reversing atherosclerosis. We showed that CD treatment of murine atherosclerosis reduced atherosclerotic plaque size and CC load and promoted plaque regression even with a continued cholesterol-rich diet. Mechanistically, CD increased oxysterol production in both macrophages and human atherosclerotic plaques and promoted liver X receptor (LXR)-mediated transcriptional reprogramming to improve cholesterol efflux and exert anti-inflammatory effects. In vivo, this CD-mediated LXR agonism was required for the antiatherosclerotic and anti-inflammatory effects of CD as well as for augmented reverse cholesterol transport. Because CD treatment in humans is safe and CD beneficially affects key mechanisms of atherogenesis, it may therefore be used clinically to prevent or treat human atherosclerosis.
Copyright © 2016, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
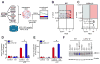
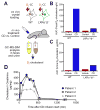
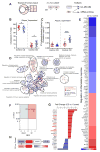
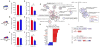
Comment in
-
Cardiovascular endocrinology: Sugar drug reverses atherosclerosis.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2016 Jun;12(6):310. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2016.62. Epub 2016 Apr 22. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2016. PMID: 27109781 No abstract available.
-
Macrophages: Dissolving cholesterol to unclog arteries.Nat Rev Immunol. 2016 Apr 28;16(5):274-5. doi: 10.1038/nri.2016.50. Nat Rev Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27121648 No abstract available.
References
-
- Robinson JG, Farnier M, Krempf M, Bergeron J, Luc G, Averna M, Stroes ES, Langslet G, Raal FJ, Shahawy ME, Koren MJ, Lepor NE, Lorenzato C, Pordy R, Chaudhari U, Kastelein JJP. ODYSSEY LONG TERM Investigators, Efficacy and Safety of Alirocumab in Reducing Lipids and Cardiovascular Events. N Engl J Med. 2015 doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1501031. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sabatine MS, Giugliano RP, Wiviott SD, Raal FJ, Blom DJ, Robinson J, Ballantyne CM, Somaratne R, Legg J, Wasserman SM, Scott R, Koren MJ, Stein EA. Open-Label Study of Long-Term Evaluation against LDL Cholesterol (OSLER) Investigators, Efficacy and Safety of Evolocumab in Reducing Lipids and Cardiovascular Events. N Engl J Med. 2015 150315080057008. - PubMed
-
- Task Force Members, ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines (CPG) Montalescot G, Sechtem U, Achenbach S, Andreotti F, Arden C, Budaj A, Bugiardini R, Crea F, Cuisset T, Di Mario C, Ferreira JR, Gersh BJ, Gitt K, Hulot JS, Marx N, Opie LH, Pfisterer M, Prescott E, Ruschitzka F, Sabate M, Senior R, Taggart DP, van der Wall EE, Vrints CJM, Zamorano JL, Baumgartner H, Bax JJ, Bueno H, Dean V, Deaton C, Erol C, Fagard R, Ferrari R, Hasdai D, Hoes AW, Kirchhof P, Knuuti J, Kolh P, Lancellotti P, Linhart A, Nihoyannopoulos P, Piepoli MF, Ponikowski P, Sirnes PA, Tamargo JL, Tendera M, Torbicki A, Wijns W, Windecker S, Valgimigli M, Bueno H, Claeys MJ, Donner-Banzhoff N, Erol C, Frank H, Funck-Brentano C, Gaemperli O, Gonzalez-Juanatey JR, Hamilos M, Husted S, James SK, Kervinen K, Kristensen SD, Maggioni AP, Piepoli MF, Pries AR, Romeo F, Ryden L, Simoons ML, Steg PG, Timmis A, Yildirir A. 2013 ESC guidelines on the management of stable coronary artery disease: The Task Force on the management of stable coronary artery disease of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur Heart J. 2013;34:2949–3003. Document Reviewers. - PubMed
-
- Sheedy FJ, Grebe A, Rayner KJ, Kalantari P, Ramkhelawon B, Carpenter SB, Becker CE, Ediriweera HN, Mullick AE, Golenbock DT, Stuart LM, Latz E, Fitzgerald KA, Moore KJ. CD36 coordinates NLRP3 inflammasome activation by facilitating intracellular nucleation of soluble ligands into particulate ligands in sterile inflammation. Nat Immunol. 2013;14:812–820. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Duewell P, Kono H, Rayner KJ, Sirois CM, Vladimer G, Bauernfeind FG, Abela GS, Franchi L, Nuñez G, Schnurr M, Espevik T, Lien E, Fitzgerald KA, Rock KL, Moore KJ, Wright SD, Hornung V, Latz E. NLRP3 inflammasomes are required for atherogenesis and activated by cholesterol crystals. Nature. 2010;464:1357–1361. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

