Association Between Menopausal Estrogen-Only Therapy and Ovarian Carcinoma Risk
- PMID: 27054934
- PMCID: PMC4892111
- DOI: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000001387
Association Between Menopausal Estrogen-Only Therapy and Ovarian Carcinoma Risk
Abstract
Objective: To describe the association between postmenopausal estrogen-only therapy use and risk of ovarian carcinoma, specifically with regard to disease histotype and duration and timing of use.
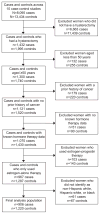
Methods: We conducted a pooled analysis of 906 women with ovarian carcinoma and 1,220 women in a control group; all 2,126 women included reported having had a hysterectomy. Ten population-based case-control studies participating in the Ovarian Cancer Association Consortium, an international consortium whose goal is to combine data from many studies with similar methods so reliable assessments of risk factors can be determined, were included. Self-reported questionnaire data from each study were harmonized and conditional logistic regression was used to examine estrogen-only therapy's histotype-specific and duration and recency of use associations.
Results: Forty-three and a half percent of the women in the control group reported previous use of estrogen-only therapy. Compared with them, current or recent estrogen-only therapy use was associated with an increased risk for the serous (51.4%, odds ratio [OR] 1.63, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.27-2.09) and endometrioid (48.6%, OR 2.00, 95% CI 1.17-3.41) histotypes. In addition, statistically significant trends in risk according to duration of use were seen among current or recent postmenopausal estrogen-only therapy users for both ovarian carcinoma histotypes (Ptrend<.001 for serous and endometrioid). Compared with women in the control group, current or recent users for 10 years or more had increased risks of serous ovarian carcinoma (36.8%, OR 1.73, 95% CI 1.26-2.38) and endometrioid ovarian carcinoma (34.9%, OR 4.03, 95% CI 1.91-8.49).
Conclusion: We found evidence of an increased risk of serous and endometrioid ovarian carcinoma associated with postmenopausal estrogen-only therapy use, particularly of long duration. These findings emphasize that risk may be associated with extended estrogen-only therapy use.
References
-
- Rossouw JE, Anderson GL, Prentice RL, et al. Risks and benefits of estrogen plus progestin in healthy postmenopausal women: principal results From the Women’s Health Initiative randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2002;288(3):321–333. - PubMed
-
- Hersh AL, Stefanick ML, Stafford RS. National use of postmenopausal hormone therapy: annual trends and response to recent evidence. JAMA. 2004;291(1):47–53. - PubMed
-
- Morch LS, Lokkegaard E, Andreasen AH, Kruger-Kjaer S, Lidegaard O. Hormone therapy and ovarian cancer. JAMA. 2009;302(3):298–305. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA136891/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA087538/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA080742/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA074850/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA105009/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA014089/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA054419/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA076016/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 ES013678/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA017054/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA126841/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 PC067010/PC/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA159981/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA046592/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000056/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA095023/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R03 CA113148/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA058598/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K07 CA080668/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA141154/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R03 CA115195/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG061132/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA071789/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA112523/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical