Mapping of the Allosteric Site in Cholesterol Hydroxylase CYP46A1 for Efavirenz, a Drug That Stimulates Enzyme Activity
- PMID: 27056331
- PMCID: PMC4882454
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M116.723577
Mapping of the Allosteric Site in Cholesterol Hydroxylase CYP46A1 for Efavirenz, a Drug That Stimulates Enzyme Activity
Abstract
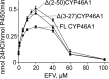
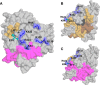
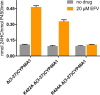
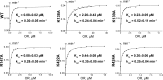
Cytochrome P450 46A1 (CYP46A1) is a microsomal enzyme and cholesterol 24-hydroxylase that controls cholesterol elimination from the brain. This P450 is also a potential target for Alzheimer disease because it can be activated pharmacologically by some marketed drugs, as exemplified by efavirenz, the anti-HIV medication. Previously, we suggested that pharmaceuticals activate CYP46A1 allosterically through binding to a site on the cytosolic protein surface, which is different from the enzyme active site facing the membrane. Here we identified this allosteric site for efavirenz on CYP46A1 by using a combination of hydrogen-deuterium exchange coupled to MS, computational modeling, site-directed mutagenesis, and analysis of the CYP46A1 crystal structure. We also mapped the binding region for the CYP46A1 redox partner oxidoreductase and found that the allosteric and redox partner binding sites share a common border. On the basis of the data obtained, we propose the mechanism of CYP46A1 allostery and the pathway for the signal transmission from the P450 allosteric site to the active site.
Keywords: Alzheimer disease; allosteric regulation; brain; cholesterol; cholesterol metabolism; cytochrome P450; drug design; hydrogen-deuterium exchange.
© 2016 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures



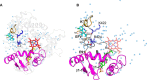
References
-
- Björkhem I., Lütjohann D., Diczfalusy U., Ståhle L., Ahlborg G., and Wahren J. (1998) cholesterol homeostasis in human brain: turnover of 24s-hydroxycholesterol and evidence for a cerebral origin of most of this oxysterol in the circulation. J. Lipid Res. 39, 1594–1600 - PubMed
-
- Lund E. G., Xie C., Kotti T., Turley S. D., Dietschy J. M., and Russell D. W. (2003) Knockout of the cholesterol 24-hydroxylase gene in mice reveals a brain-specific mechanism of cholesterol turnover. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 22980–22988 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

