Fabrication, characterization, and evaluation of microsponge delivery system for facilitated fungal therapy
- PMID: 27057125
- PMCID: PMC4804404
- DOI: 10.4103/0976-0105.177705
Fabrication, characterization, and evaluation of microsponge delivery system for facilitated fungal therapy
Abstract
Objective: The rationale behind present research vocation was to develop and investigate a novel microsponge based gel as a topical carrier for the prolonged release and cutaneous drug deposition of fluconazole (FLZ); destined for facilitated fungal therapy.
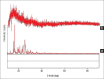
Materials and methods: Microsponges were prepared using quasi-emulsion solvent diffusion method using Eudragit S-100. In the direction of optimization, the effect of formulation variables (drug-polymer ratio and amount of emulsifier) and diverse factors affecting physical characteristics of microsponge were investigated as well. Fabricated microsponges were characterized by differential scanning calorimetry, Fourier transform-infrared, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), particle size analysis, and also evaluated for drug content, encapsulation efficiency, in vitro drug release and in vitro antifungal activity.
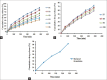
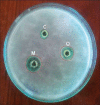
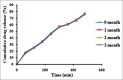
Results: Compatibility studies results reflected no sign of any chemical interaction between the drug and polymers used. Whereas, varied drug-polymer ratios and emulsifier concentration indicated significant effect on production yield, drug content, encapsulation efficiency, particle size and drug release. Spherical microsponges with a porous surface and 29.327 ± 0.31 μm mean particle size were evident from SEM micrographs. In vitro release outcomes, from microsponge loaded gels depicted that F1 formulation was more efficient to give extended drug release of 85.38% at the end of 8 h, while conventional formulation by releasing 83.17% of drug got exhausted incredibly earlier at the end of 4 h merely. Moreover, microsponge gels demonstrated substantial spreadability and extrudability along with promising antifungal activity.
Conclusions: Fabricated microsponges would be impending pharmaceutical topical carriers of FLZ and a leading alternative to conventional therapy for efficient, safe and facilitated eradication of fungal infections.
Keywords: Drug delivery; fluconazole; gel; microsponges; sustained release.
Figures



References
-
- Gupta M, Goyal AK, Paliwal SR, Paliwal R, Mishra N, Vaidya B, et al. Development and characterization of effective topical liposomal system for localized treatment of cutaneous candidiasis. J Liposome Res. 2010;20:341–50. - PubMed
-
- Bidkar S, Jain D, Padsalg A, Patel K, Mokale V. Formulation development and evaluation of fluconazole gel in various polymer bases. Asian J Pharm. 2007;1:63–8.
-
- Schäfer-Korting M, Mehnert W, Korting HC. Lipid nanoparticles for improved topical application of drugs for skin diseases. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2007;59:427–43. - PubMed
-
- Osmani RA, Aloorkar NH, Kulkarni AS, Harkare BR, Bhosale RR. A new cornucopia in topical drug delivery: Microsponge technology. Asian J Pharm Sci Tech. 2014;4:48–60.
-
- Teichmann A, Heuschkel S, Jacobi U, Presse G, Neubert RH, Sterry W, et al. Comparison of stratum corneum penetration and localization of a lipophilic model drug applied in an o/w microemulsion and an amphiphilic cream. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2007;67:699–706. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
