Two Traditional Chinese Medicines Curcumae Radix and Curcumae Rhizoma: An Ethnopharmacology, Phytochemistry, and Pharmacology Review
- PMID: 27057197
- PMCID: PMC4775794
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/4973128
Two Traditional Chinese Medicines Curcumae Radix and Curcumae Rhizoma: An Ethnopharmacology, Phytochemistry, and Pharmacology Review
Abstract
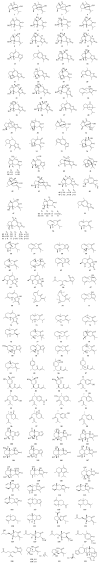
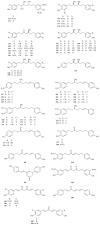
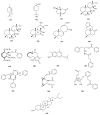
Curcumae Rhizoma, known as Ezhu (Chinese: ), and Curcumae Radix, known as Yujin (Chinese: ), are different plant parts coming from three same species according to China Pharmacopoeia. Actually, they are used in different ways in TCM clinical treatment. Curcumae Rhizoma is mainly used as antitumor drug, while Curcumae Radix has been used as antidepressant and cholagogue. Curcumae Rhizoma and Curcumae Radix are confused in variety and source, even in clinical trials by some nonprofessional workers. So it is important for us to make them clear. This review is aimed at summarizing the ethnopharmacology, phytochemical, and pharmacological differences between Curcumae Radix and Curcumae Rhizoma by SciFinder, CNKI, and so on, to use them exactly and clearly. Further studies on Curcumae Rhizoma and Curcumae Radix can lead to the development of new drugs and therapeutics for various diseases on the basis of the TCM theory.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Herb pairs containing Curcumae Rhizoma (Ezhu): A review of bio-active constituents, compatibility effects and t-copula function analysis.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Jan 30;319(Pt 3):117199. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.117199. Epub 2023 Oct 14. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37844744 Review.
-
Curcumae Radix: a review of its botany, traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacology and toxicology.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2022 Jun 9;74(6):779-792. doi: 10.1093/jpp/rgab126. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34633034 Review.
-
Extracts from Huangqi (Radix Astragali Mongoliciplus) and Ezhu (Rhizoma Curcumae Phaeocaulis) inhibit Lewis lung carcinoma cell growth in a xenograft mouse model by impairing mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling, vascular endothelial growth factor production, and angiogenesis.J Tradit Chin Med. 2019 Aug;39(4):559-565. J Tradit Chin Med. 2019. PMID: 32186104
-
Sources, morphology, phytochemistry, pharmacology of Curcumae Longae Rhizoma, Curcumae Radix, and Curcumae Rhizoma: a review of the literature.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Aug 31;14:1229963. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1229963. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37719857 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Nature-effect relationship research of Curcumae Longae Rhizoma,Curcumae Radix,and Curcumae Rhizoma based on nature combination].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2019 Jan;44(2):229-234. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20180903.003. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 30989938 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Curdione Induces Antiproliferation Effect on Human Uterine Leiomyosarcoma via Targeting IDO1.Front Oncol. 2021 Feb 26;11:637024. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.637024. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33718227 Free PMC article.
-
Yifei Sanjie Formula Treats Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease by Remodeling Pulmonary Microbiota.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Jun 29;9:927607. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.927607. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35847812 Free PMC article.
-
Unlocking the Potential of Curcumae Rhizoma Aqueous Extract in Stress Resistance and Extending Lifespan in Caenorhabditis elegans.Molecules. 2025 Apr 8;30(8):1668. doi: 10.3390/molecules30081668. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40333562 Free PMC article.
-
The analgesic effects of β-elemene in rats with neuropathic pain by inhibition of spinal astrocytic ERK activation.Mol Pain. 2022 Apr;18:17448069221121562. doi: 10.1177/17448069221121562. Mol Pain. 2022. PMID: 35976914 Free PMC article.
-
General Use of Chinese Herbal Products among Female Patients with Mastitis in Taiwan.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Mar 25;2022:3876240. doi: 10.1155/2022/3876240. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35368771 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Committee for the Pharmacopoeia of PR China. Pharmacopoeia of PR China. part I. Beijing, China: China Medical Science and Technology Press; 2010.
-
- Xia Q., Huang Z.-G., Li S.-P., Zhang P., Wang J., He L.-N. The experiment study of the antivirus effects of zedoary oil on influenzavirus and respiratory syncytial virus. Chinese Pharmacological Bulletin. 2004;20(3):357–358.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

