Effects of comorbid conditions on health-related quality of life in youth with Type 2 diabetes: the TODAY clinical trial
- PMID: 27057209
- PMCID: PMC4820314
- DOI: 10.2217/dmt.15.35
Effects of comorbid conditions on health-related quality of life in youth with Type 2 diabetes: the TODAY clinical trial
Abstract
Aim: To explore associations between health-related quality of life (HRQOL) and comorbidities in youth with Type 2 diabetes.
Patients & methods: Of 699 youth in the TODAY study, 685 (98%) had baseline HRQOL data, 649 (93%) at 6 months and 583 (83%) at 24 months. Comorbidities were defined by sustained abnormal values and treatment regimens.
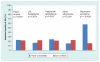
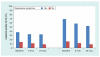
Results: At baseline, 22.2% of participants demonstrated impaired HRQOL. Only depressive symptoms distinguished those with versus without impaired HRQOL and were significantly related to later impaired HRQOL (p < 0.0001). A significant correspondence between impaired HRQOL and number of comorbidities (p = 0.0003) was noted, but was driven by the presence of depressive symptoms.
Conclusion: Results emphasize the need for evaluation of depressive symptoms. Other comorbidities did not have a significant impact on HRQOL in this cohort.
Keywords: health-related quality of life; hyperlipidemia; hypertension; microalbuminuria; pediatric Type 2 diabetes.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Longitudinal Association of Depressive Symptoms, Binge Eating, and Quality of Life With Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Young Adults With Youth-Onset Type 2 Diabetes: The TODAY2 Study.Diabetes Care. 2022 Mar 15;45(5):1073-81. doi: 10.2337/dc21-1995. Online ahead of print. Diabetes Care. 2022. PMID: 35290434 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired health-related quality of life in Addison's disease--impact of replacement therapy, comorbidities and socio-economic factors.Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2014 Oct;81(4):511-8. doi: 10.1111/cen.12484. Epub 2014 Jun 12. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2014. PMID: 24801591
-
Predictors of health-related quality of life in obese youth.Obesity (Silver Spring). 2006 Jan;14(1):122-30. doi: 10.1038/oby.2006.15. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2006. PMID: 16493130
-
Assessment of health-related quality of life of clients in vocational rehabilitation: association with depressive symptoms and type of services.Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2014 Jun;50(3):343-53. Epub 2013 Dec 5. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2014. PMID: 24309502
-
Comorbidities and predictors of health-related quality of life in Dravet syndrome.Epilepsia. 2011 Aug;52(8):1476-82. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2011.03129.x. Epub 2011 Jun 10. Epilepsia. 2011. PMID: 21668444
Cited by
-
The Prevalence of Obesity Among Children With Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.JAMA Netw Open. 2022 Dec 1;5(12):e2247186. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.47186. JAMA Netw Open. 2022. PMID: 36520430 Free PMC article.
-
Predictors of Health-Related Quality of Life Among Patients with Type II Diabetes Mellitus Who Are Insulin Users: A Multidimensional Model.Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 2019 Apr 25;90:53-60. doi: 10.1016/j.curtheres.2019.04.001. eCollection 2019. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 2019. PMID: 31193026 Free PMC article.
-
Co-Morbidities and Sex Differences in Long-Term Quality-of-Life Outcomes among Patients with and without Diabetes after Total Knee Replacement: Five-Year Data from Registry Study.J Clin Med. 2019 Dec 19;9(1):19. doi: 10.3390/jcm9010019. J Clin Med. 2019. PMID: 31861688 Free PMC article.
-
Non-Exercise Based Estimation of Cardiorespiratory Fitness Mediates Associations between Comorbidities and Health-Related Quality of Life in Older Korean Adults with Diabetes.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Feb 12;17(4):1164. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17041164. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32059584 Free PMC article.
-
Barriers and Facilitators to Incorporating an Integrative Mind-Body Intervention in Youth With Type 2 Diabetes.JAACAP Open. 2024 Feb 15;2(3):208-216. doi: 10.1016/j.jaacop.2024.01.005. eCollection 2024 Sep. JAACAP Open. 2024. PMID: 39552817 Free PMC article.
References
-
-
TODAY Study Group Rapid rise in hypertension and nephropathy in youth with Type 2 diabetes: the TODAY clinical trial. Diabetes Care. 2013;36(6):1735–1741. • Provides background and details of the TODAY clinical trial.
-
-
-
TODAY Study Group Lipid and inflammatory cardiovascular risk worsens over 3 years in youth with Type 2 diabetes: the TODAY clinical trial. Diabetes Care. 2013;36(6):1758–1764. • Provides background and details of the TODAY clinical trial.
-
-
-
Copeland KC, Silverstein J, Moore KR, et al. Management of newly diagnosed Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in children and adolescents. Pediatrics. 2013;131(2):364–382. • Provides background and details of the TODAY clinical trial.
-
-
-
Copeland KC, Zeitler P, Geffner M, et al. Characteristics of adolescents and youth with recent-onset Type 2 diabetes: the TODAY cohort at baseline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011;96(1):159–167. • Provides background and details of the TODAY clinical trial.
-
-
-
Rodriguez BL, Dabelea D, Liese AD, et al. Prevalence and correlates of elevated blood pressure in youth with diabetes mellitus: the SEARCH for diabetes in youth study. J. Pediatr. 2010;157(2):245–251. • Describe similar studies and results performed in other populations.
-
Grants and funding
- U01 DK061254/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024139/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024989/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024153/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025780/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000069/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000036/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061242/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024992/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061212/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR001066/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR014467/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061230/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000043/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025758/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000084/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000125/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061239/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024134/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
