Molecular and pharmacodynamic interactions between caffeine and dopaminergic system
- PMID: 27057246
- PMCID: PMC4813614
Molecular and pharmacodynamic interactions between caffeine and dopaminergic system
Abstract
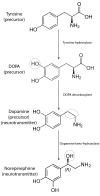
Many drugs targeting dopaminergic system were developed for treating schizophrenia (antagonists of D2 dopaminergic receptors, e.g. antipsychotics) or Parkinson' disease (agonists of dopaminergic receptors, e.g. L-DOPA). Because many of the patients treated with these drugs consume caffeine based beverages, pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics interactions between caffeine and dopaminergic system or drugs influencing this system are possible. The present review is assessing the current available scientific data on pharmacodynamics interactions between the dopaminergic and adenosinergic system but also on caffeine and dopaminergic system interactions. Caffeine can significantly improve Parkinson's disease symptoms but also the extrapyramidal syndrome induced by antipsychotics via dopaminergic pathways. No study so far has directly evaluated the influence of caffeine in schizophrenia, but there is growing evidence that adenosine dysfunction may contribute to the neurobiological and clinical features of schizophrenia. Caffeine has also effects on the reward system but it seems that this effect does not involve dopaminergic system. Caffeine has some endocrine effects via dopaminergic system such as decreasing the milk production in lactating women or other potential reproductive and nutritional consequences.
Keywords: Parkinson; adenosine; caffeine; dopamine; schizophrenia.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Caffeine-induced locomotor activity: possible involvement of GABAergic-dopaminergic-adenosinergic interaction.Neurochem Res. 1995 Jan;20(1):39-44. doi: 10.1007/BF00995150. Neurochem Res. 1995. PMID: 7739757
-
Adenosine receptor blockade reverses hypophagia and enhances locomotor activity of dopamine-deficient mice.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Feb 4;100(3):1346-51. doi: 10.1073/pnas.252753799. Epub 2003 Jan 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 12538862 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of adenosine receptors with other receptors from therapeutic perspective in Parkinson's disease.Int Rev Neurobiol. 2014;119:151-67. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-801022-8.00007-6. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2014. PMID: 25175965
-
Astra Award Lecture. Adenosine, adenosine receptors and the actions of caffeine.Pharmacol Toxicol. 1995 Feb;76(2):93-101. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1995.tb00111.x. Pharmacol Toxicol. 1995. PMID: 7746802 Review.
-
Caffeine and adenosine.J Alzheimers Dis. 2010;20 Suppl 1:S3-15. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2010-1379. J Alzheimers Dis. 2010. PMID: 20164566 Review.
Cited by
-
The Influence of a Xanthine-Catechin Chemical Matrix on in vitro Macrophage-Activation Triggered by Antipsychotic Ziprasidone.Inflammation. 2019 Jun;42(3):915-925. doi: 10.1007/s10753-018-0946-9. Inflammation. 2019. PMID: 30547260
References
-
- Dahlstroem A, Fuxe K, Olson L, Ungerstedt U. Ascending systems of catecholamine neurons from the lower brain stem. Acta Physiol Scand. 1964 Dec;62:485–486. - PubMed
-
- Fulga I. Farmacologie. Ed. Medicala: 2004. pp. 189–191.
-
- Kebabian JW, Calne DB. Multiple receptors for dopamine. Nature. 1979 Jan 11;277(5692):93–96. - PubMed
-
- Beaulieu JM1, Gainetdinov RR. The physiology, signaling, and pharmacology of dopamine receptors. Pharmacol Rev. 2011 Mar;63(1):182–217. doi: 10.1124/pr.110.002642. Epub 2011 Feb 8. - PubMed
-
- Beninger RJ. The role of dopamine in locomotor activity and learning. Brain Res. 1983 Oct;287(2):173–196. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical