Host nucleotide polymorphism in hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 27057306
- PMCID: PMC4820640
- DOI: 10.4254/wjh.v8.i10.485
Host nucleotide polymorphism in hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
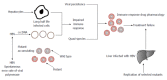
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is etiologically linked with hepatitis B virus (HBV) and is the leading cause of death amongst 80% of HBV patients. Among HBV affected patients, genetic factors are also involved in modifying the risk factors of HCC. However, the genetic factors that regulate progression to HCC still remain to be determined. In this review, we discuss several single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) which were reportedly associated with increased or reduced risk of HCC occurrence in patients with chronic HBV infection such as cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 expression specifically at COX-2 -1195G/A in Chinese, Turkish and Egyptian populations, tumor necrosis factor α and the three most commonly studied SNPs: PAT-/+, Lys939Gln (A33512C, rs2228001) and Ala499Val (C21151T, rs2228000). In genome-wide association studies, strong associations have also been found at loci 1p36.22, 11q22.3, 6p21 (rs1419881, rs3997872, rs7453920 and rs7768538), 8p12 (rs2275959 and rs37821974) and 22q11.21. The genes implicated in these studies include HLA-DQB2, HLA-DQA1, TCF19, HLA-C, UBE2L3, LTL, FDX1, MICA, UBE4B and PG. The SNPs found to be associated with the above-mentioned genes still require validation in association studies in order to be considered good prognostic candidates for HCC. Screening of these polymorphisms is very beneficial in clinical experiments to stratify the higher or lower risk for HCC and may help in designing effective and efficient HCC surveillance programs for chronic HBV-infected patients if further genetic vulnerabilities are detected.
Keywords: Genetic polymorphism; Hepatitis B virus; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Liver cirrhosis; Subtypes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Variants identified by hepatocellular carcinoma and chronic hepatitis B virus infection susceptibility GWAS associated with survival in HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma.PLoS One. 2014 Jul 2;9(7):e101586. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0101586. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24987808 Free PMC article.
-
Single nucleotide polymorphisms associated with hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection.Intervirology. 2005;48(1):10-5. doi: 10.1159/000082089. Intervirology. 2005. PMID: 15785084 Review.
-
Genetic variants in the 6p21.3 region influence hepatitis B virus clearance and chronic hepatitis B risk in the Han Chinese population.Liver Res. 2024 Feb 29;8(1):54-60. doi: 10.1016/j.livres.2024.02.001. eCollection 2024 Mar. Liver Res. 2024. PMID: 39959030 Free PMC article.
-
[Genetic epidemiological study on single nucleotide polymorphisms associated with hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic HBV infection].Korean J Hepatol. 2009 Mar;15(1):7-14. doi: 10.3350/kjhep.2009.15.1.7. Korean J Hepatol. 2009. PMID: 19346781 Review. Korean.
-
Genetic variants in human leukocyte antigen/DP-DQ influence both hepatitis B virus clearance and hepatocellular carcinoma development.Hepatology. 2012 May;55(5):1426-31. doi: 10.1002/hep.24799. Epub 2012 Mar 16. Hepatology. 2012. PMID: 22105689
Cited by
-
Comprehensive investigation of cytokine- and immune-related gene variants in HBV-associated hepatocellular carcinoma patients.Biosci Rep. 2017 Dec 12;37(6):BSR20171263. doi: 10.1042/BSR20171263. Print 2017 Dec 22. Biosci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29138264 Free PMC article.
-
Current status of ctDNA in precision oncology for hepatocellular carcinoma.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Apr 26;40(1):140. doi: 10.1186/s13046-021-01940-8. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33902698 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Micro-RNA-21 rs1292037 A>G polymorphism can predict hepatocellular carcinoma prognosis (HCC), and plays a key role in cell proliferation and ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI) in HCC cell model of IRI.Saudi Med J. 2020 Apr;41(4):383-392. doi: 10.15537/smj.2020.4.24994. Saudi Med J. 2020. PMID: 32291425 Free PMC article.
-
Authorship Patterns in Cancer Genomics Publications Across Africa.JCO Glob Oncol. 2021 May;7:747-755. doi: 10.1200/GO.20.00552. JCO Glob Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34033494 Free PMC article.
-
Host Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms Modulating Influenza A Virus Disease in Humans.Pathogens. 2019 Sep 30;8(4):168. doi: 10.3390/pathogens8040168. Pathogens. 2019. PMID: 31574965 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lai CL, Ratziu V, Yuen MF, Poynard T. Viral hepatitis B. Lancet. 2003;362:2089–2094. - PubMed
-
- Yim HJ, Lok AS. Natural history of chronic hepatitis B virus infection: what we knew in 1981 and what we know in 2005. Hepatology. 2006;43:S173–S181. - PubMed
-
- Sherman M. Hepatocellular carcinoma: epidemiology, surveillance, and diagnosis. Semin Liver Dis. 2010;30:3–16. - PubMed
-
- Paterlini-Bréchot P, Saigo K, Murakami Y, Chami M, Gozuacik D, Mugnier C, Lagorce D, Bréchot C. Hepatitis B virus-related insertional mutagenesis occurs frequently in human liver cancers and recurrently targets human telomerase gene. Oncogene. 2003;22:3911–3916. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous