Dietary flavonoid fisetin for cancer prevention and treatment
- PMID: 27059089
- PMCID: PMC6261287
- DOI: 10.1002/mnfr.201600025
Dietary flavonoid fisetin for cancer prevention and treatment
Abstract
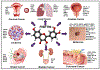
Cancer remains a major public health concern and a significant cause of death worldwide. Identification of bioactive molecules that have the potential to inhibit carcinogenesis continues to garner interest among the scientific community. In particular, flavonoids from dietary sources are the most sought after because of their safety, cost-effectiveness, and feasibility of oral administration. Emerging data have provided newer insights into understanding the molecular mechanisms that are essential to identify novel mechanism-based strategies for cancer prevention and treatment. Dietary flavonoid fisetin (3,3',4',7-tetrahydroxyflavone) found in many fruits and vegetables has been shown in preclinical studies to inhibit cancer growth through alteration of cell cycle, inducing apoptosis, angiogenesis, invasion, and metastasis without causing any toxicity to normal cells. Although data from in-vitro and in-vivo studies look convincing, well-designed clinical trials in humans are needed to conclusively determine the efficacy across various cancers. This review highlights the chemopreventive and therapeutic effects, molecular targets, and mechanisms that contribute to the observed anticancer activity of fisetin against various cancers.
Keywords: Cancer; Chemoprevention; Diet; Fisetin; Flavonoid.
© 2016 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Figures
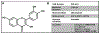
Similar articles
-
Fisetin: A bioactive phytochemical with potential for cancer prevention and pharmacotherapy.Life Sci. 2018 Feb 1;194:75-87. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2017.12.005. Epub 2017 Dec 7. Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 29225112 Review.
-
Exploring the molecular targets of dietary flavonoid fisetin in cancer.Semin Cancer Biol. 2016 Oct;40-41:130-140. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2016.04.003. Epub 2016 May 6. Semin Cancer Biol. 2016. PMID: 27163728 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fisetin: a dietary antioxidant for health promotion.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013 Jul 10;19(2):151-62. doi: 10.1089/ars.2012.4901. Epub 2012 Dec 18. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013. PMID: 23121441 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemopreventive effect of dietary polyphenols in colorectal cancer cell lines.Nutr Res. 2011 Feb;31(2):77-87. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2011.01.006. Nutr Res. 2011. PMID: 21419311 Review.
-
Cancer chemoprevention and chemotherapy: dietary polyphenols and signalling pathways.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2008 May;52(5):507-26. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.200700326. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2008. PMID: 18435439 Review.
Cited by
-
Flavonoids Targeting the mTOR Signaling Cascades in Cancer: A Potential Crosstalk in Anti-Breast Cancer Therapy.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Jun 27;2022:4831833. doi: 10.1155/2022/4831833. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35795855 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fisetin's Promising Antitumor Effects: Uncovering Mechanisms and Targeting for Future Therapies.Glob Med Genet. 2023 Aug 9;10(3):205-220. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-1772219. eCollection 2023 Sep. Glob Med Genet. 2023. PMID: 37565061 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The PI3K-Akt-mTOR and Associated Signaling Pathways as Molecular Drivers of Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Skin Diseases: Update on Therapeutic Strategy Using Natural and Synthetic Compounds.Cells. 2023 Jun 20;12(12):1671. doi: 10.3390/cells12121671. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37371141 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel triazole analogs of apigenin-7-methyl ether exhibit potent antitumor activity against ovarian carcinoma cells via the induction of mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis.Exp Ther Med. 2019 Mar;17(3):1670-1676. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.7138. Epub 2018 Dec 28. Exp Ther Med. 2019. PMID: 30783435 Free PMC article.
-
Apigenin exerts chemopreventive effects on lung injury induced by SiO2 nanoparticles through the activation of Nrf2.J Nat Med. 2022 Jan;76(1):119-131. doi: 10.1007/s11418-021-01561-7. Epub 2021 Sep 4. J Nat Med. 2022. PMID: 34480707
References
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J et al., Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians 2015, 65, 87–108. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A, Cancer statistics, 2015. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians 2015, 65, 5–29. - PubMed
-
- Singh SR, Cancer stem cells: recent developments and future prospects. Cancer Letters 2013, 338, 1–2. - PubMed
-
- Kasala ER, Bodduluru LN, Madana RM, V AK et al., Chemopreventive and therapeutic potential of chrysin in cancer: mechanistic perspectives. Toxicology Letters 2015, 233, 214–225. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

