Increased lethality and defective pulmonary clearance of Streptococcus pneumoniae in microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1-knockout mice
- PMID: 27059285
- PMCID: PMC4935474
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00220.2015
Increased lethality and defective pulmonary clearance of Streptococcus pneumoniae in microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1-knockout mice
Abstract
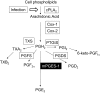
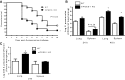
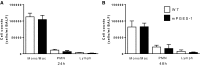
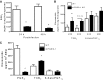
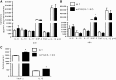
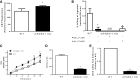
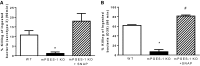
The production of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) increases dramatically during pneumococcal pneumonia, and this lipid mediator impairs alveolar macrophage (AM)-mediated innate immune responses. Microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 (mPGES-1) is a key enzyme involved in the synthesis of PGE2, and its expression is enhanced during bacterial infections. Genetic deletion of mPGES-1 in mice results in diminished PGE2 production and elevated levels of other prostaglandins after infection. Since PGE2 plays an important immunoregulatory role during bacterial pneumonia we assessed the impact of mPGES-1 deletion in the host defense against pneumococcal pneumonia in vivo and in AMs in vitro. Wild-type (WT) and mPGES-1 knockout (KO) mice were challenged with Streptococcus pneumoniae via the intratracheal route. Compared with WT animals, we observed reduced survival and increased lung and spleen bacterial burdens in mPGES-1 KO mice 24 and 48 h after S. pneumoniae infection. While we found modest differences between WT and mPGES-1 KO mice in pulmonary cytokines, AMs from mPGES-1 KO mice exhibited defective killing of ingested bacteria in vitro that was associated with diminished inducible nitric oxide synthase expression and reduced nitric oxide (NO) synthesis. Treatment of AMs from mPGES-1 KO mice with an NO donor restored bacterial killing in vitro. These results suggest that mPGES-1 plays a critical role in bacterial pneumonia and that genetic ablation of this enzyme results in diminished pulmonary host defense in vivo and in vitro. These results suggest that specific inhibition of PGE2 synthesis by targeting mPGES-1 may weaken host defense against bacterial infections.
Keywords: Streptococcus pneumoniae; bacterial pneumonia; host defense; lung; microsomal prostaglandin E synthase; prostaglandins.
Copyright © 2016 the American Physiological Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ablation of the leptin receptor in myeloid cells impairs pulmonary clearance of Streptococcus pneumoniae and alveolar macrophage bactericidal function.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2018 Jul 1;315(1):L78-L86. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00447.2017. Epub 2018 Mar 22. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29565180 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma gelsolin improves lung host defense against pneumonia by enhancing macrophage NOS3 function.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2015 Jul 1;309(1):L11-6. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00094.2015. Epub 2015 May 8. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25957291 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of microsomal prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) synthase-1 reduces inducible and basal PGE2 production and alters the gastric prostanoid profile.J Biol Chem. 2004 May 28;279(22):23229-37. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M400443200. Epub 2004 Mar 11. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15016822
-
[The role of prostaglandin E2 in stroke-reperfusion injury].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2013;133(9):947-54. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.13-00171. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2013. PMID: 23995802 Review. Japanese.
-
Microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1: the inducible synthase for prostaglandin E2.Arthritis Res Ther. 2005;7(3):114-7. doi: 10.1186/ar1748. Epub 2005 Apr 6. Arthritis Res Ther. 2005. PMID: 15899061 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Human lung fibroblasts produce proresolving peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ ligands in a cyclooxygenase-2-dependent manner.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2016 Nov 1;311(5):L855-L867. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00272.2016. Epub 2016 Sep 9. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27612965 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) targets and mechanisms of puerarin.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Jan;25(2):677-685. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16117. Epub 2020 Nov 26. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 33241658 Free PMC article.
-
The prostaglandin D2 antagonist asapiprant ameliorates clinical severity in young hosts infected with invasive Streptococcus pneumoniae.Infect Immun. 2024 May 7;92(5):e0052223. doi: 10.1128/iai.00522-23. Epub 2024 Apr 17. Infect Immun. 2024. PMID: 38629842 Free PMC article.
-
Ablation of the leptin receptor in myeloid cells impairs pulmonary clearance of Streptococcus pneumoniae and alveolar macrophage bactericidal function.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2018 Jul 1;315(1):L78-L86. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00447.2017. Epub 2018 Mar 22. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29565180 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Bacterial Toxins in the Lungs.Toxins (Basel). 2020 Apr 2;12(4):223. doi: 10.3390/toxins12040223. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32252376 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aronoff DM, Canetti C, Peters-Golden M. Prostaglandin E2 inhibits alveolar macrophage phagocytosis through an E-prostanoid 2 receptor-mediated increase in intracellular cyclic AMP. J Immunol 173: 559–565, 2004. - PubMed
-
- Aronoff DM, Canetti C, Serezani CH, Luo M, Peters-Golden M. Cutting edge: macrophage inhibition by cyclic AMP (cAMP): differential roles of protein kinase A and exchange protein directly activated by cAMP-1. J Immunol 174: 595–599, 2005. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

